Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language that is a must for data professionals. With the rise in demand for data analysts, database administrators (DBAs), data scientists, business intelligence developers, and even software developers, it has become quite important for these professionals to get fully prepared with SQL to grab good opportunities in the field.
In that light, we have prepared this article for you that will help you prepare for a SQL interview, but before starting with the technical round, you must be prepared for some general questions, as mentioned below:
- “How long have you been working with SQL?”
- “How would you rate your proficiency in SQL on a scale?”
- “What are some common SQL syntax used for data manipulation?”
These questions might be there in your resume, but practice elaborating on them to the interviewer, as the answers to these questions are going to decide whether you will be promoted to the technical round or not.
Top 35 advanced and technical SQL interview questions to crack the technical interview rounds for MNCs
Beginner Level
1) How is SQL different from other programming languages?
You will be able to answer this basic question only if you understand the functioning of SQL and other programming languages, such as Java or Python. You may already know the answer to this, as you are preparing for the SQL round; however, for greater clarity, we will address it here. With SQL, you do not have to give step-by-step logic to the database to retrieve the result, but with languages like Java or Python, you write code to explain to the system how to do something, including loops, conditions, and memory management. An example of this description is given below.
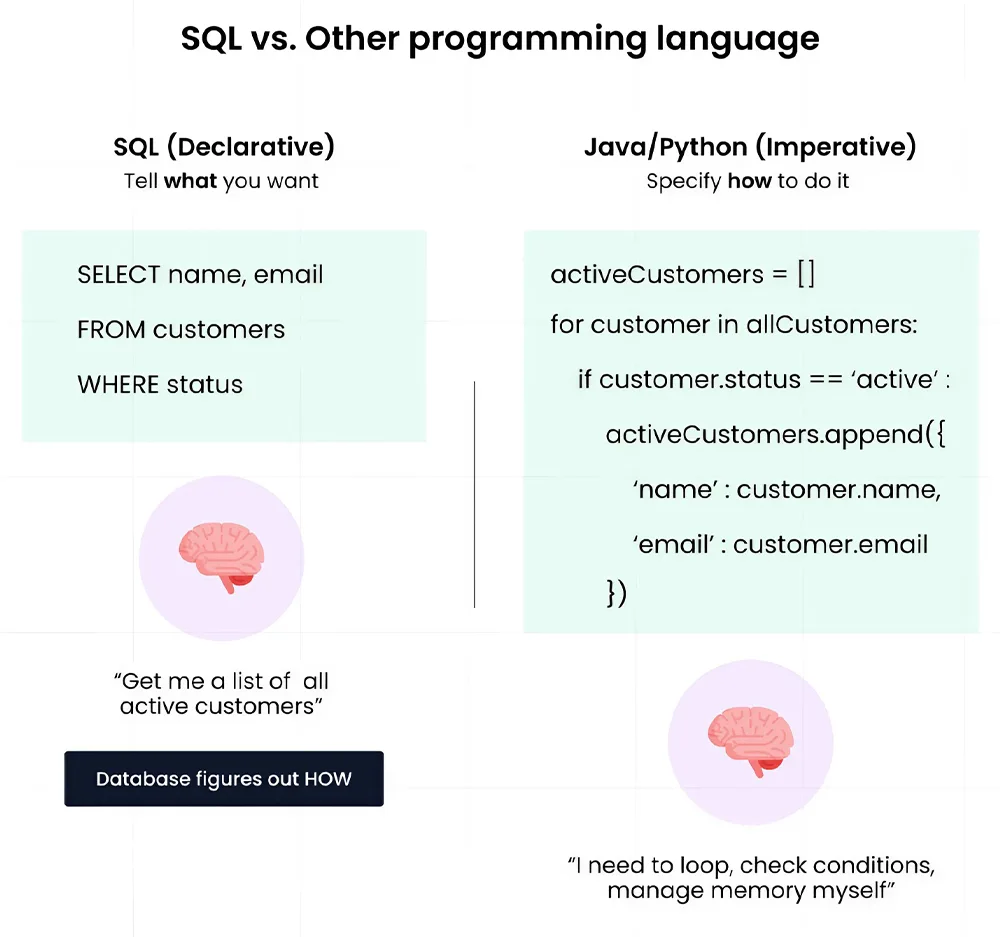
Source: roadmap.sh
2) What are the types of SQL subsets, and how are they different?
Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), and Data Control Language (DCL) are the three SQL subsets. The major difference between these subsets is in the purpose they serve:
- “DDL affects the structure of the database.”
- “DML interacts with the data itself.”
- “DCL governs who can do what within the database system.”
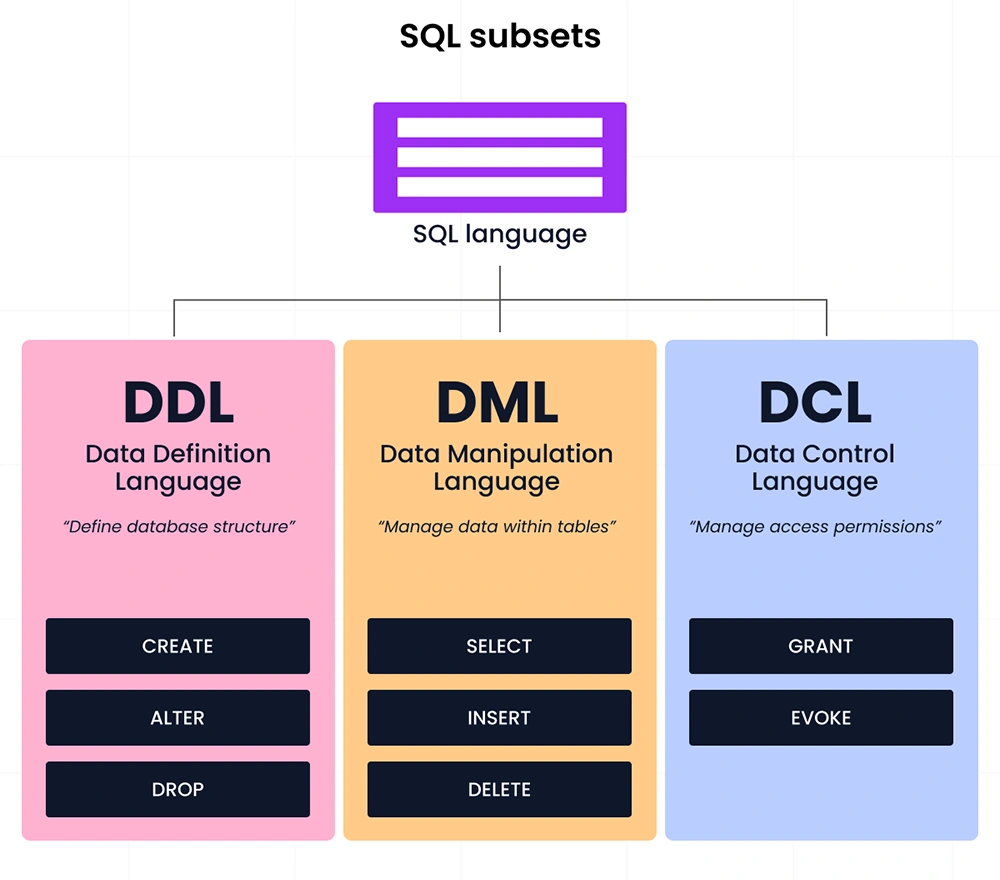
Source: roadmap.sh
3) What are SQL dialects?
SQL dialects are different segments of SQL differentiated on the basis of their functionality. These dialects work on the SQL standard only, but use different features or syntax for the same data set. Thus, based on the results you want, you can implement the SQL dialect accordingly. Some common SQL dialects include MySQL (for web applications), PostgreSQL (for advanced features and standards compliance), Microsoft SQL Server (Common in enterprise environments), and SQLite (Lightweight; used in mobile or embedded applications).
4) What is a primary key?
A primary key is used to identify each row in a table. For this to run, each row must be unique and have some value. This is one primary key constraint. Also, the row cannot contain a NULL value. An example of this explanation is provided below.
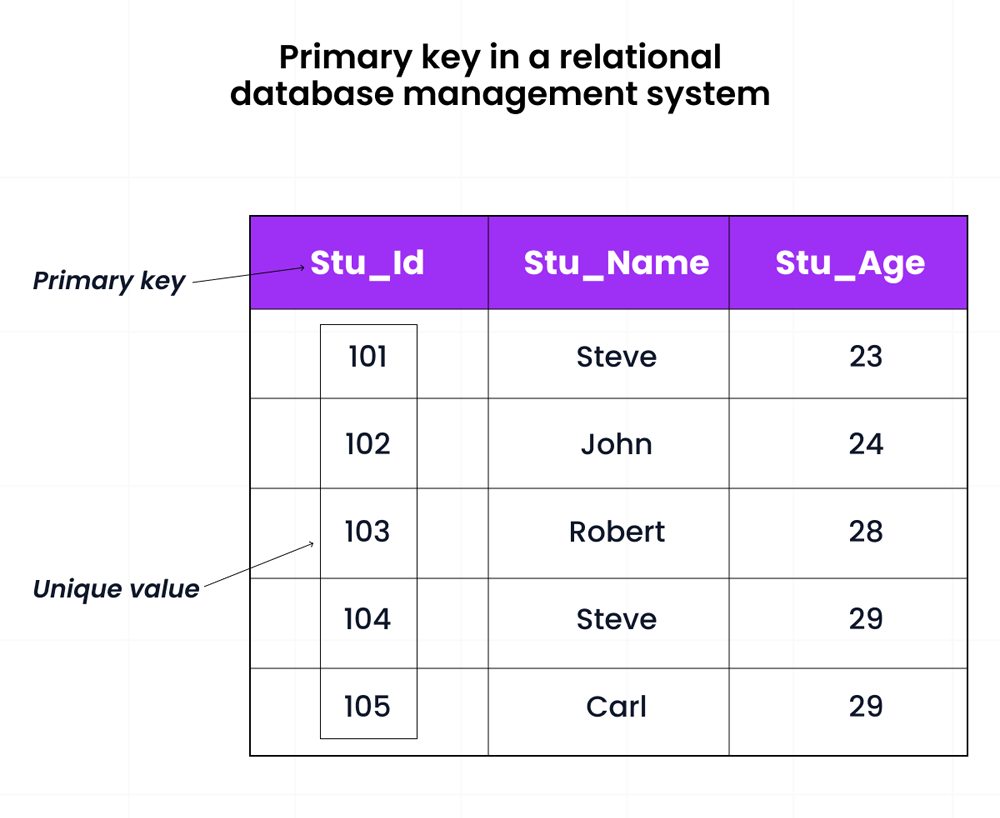
Source: roadmap.sh
5) Explain the concept of normalization in database design.
The process of organizing tables to improve data integrity and reduce redundancy is known as normalization. In this process, tables are broken down into smaller, more focused tables with defined relationships.
6) Describe the purpose of window functions in SQL.
Window functions are used to perform calculations on a set of rows. These calculations can be anything, including calculating moving averages, ranking, and finding percentiles.
7) How can you handle missing values (NULL) in your queries?
Functions like ISNULL, COALESCE, or CASE statements are used to handle missing values. These will make you add alternative values or perform different operations based on NULL checks.
8) Write a query to find the top 5 customers with the highest total order amounts.
“SQL Code
SELECT CustomerID, SUM(OrderAmount) AS TotalOrderAmount
FROM Orders
GROUP BY CustomerID
ORDER BY TotalOrderAmount DESC
LIMIT 5;”
9) How can you optimize a slow-running query?
You can answer this question as per your knowledge; however, we are putting some options here.
- “Using appropriate indexes”
- “Avoiding unnecessary joins and subqueries”
- “Using efficient functions and operators”
- “Analyzing execution plans to identify bottlenecks”
10) Explain the difference between UNION and UNION ALL in SQL.
UNION statement is used to give you unique rows from the data set by removing the duplicate rows, while the UNION ALL statement gives all the rows from the selected queries, even the duplicate ones.
Intermediate Level
11) Explain the difference between a correlated subquery and a nested subquery.
A nested subquery is an independent subquery and does not take any reference from the outer query. For example, when you find out the number of employees whose salary is greater than the overall average salary of all employees. The subquery that you run to calculate the overall average can run independently and is thus referred to as a nested subquery. A correlated subquery, as the name suggests, is dependent on the outer subquery. It takes references from one or more columns of the outer query in its WHERE clause. For example, when you find out the employees whose salary is greater than the average salary within their own department, your subquery would take reference to the department_id from the rows of the outer query; thus, it is a correlated subquery.
12) Write a query to find the average salary for each department, excluding employees with salaries above a certain threshold.
“SQL Code
SELECT Department, AVG(Salary) AS AverageSalary
FROM (
SELECT Department, Salary
FROM Employees
WHERE Salary <= (SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employees) / 2
) AS Subquery
GROUP BY Department;”
13) Describe the concept of transactions in SQL and their ACID properties.
Transactions are the single, logical unit of work in SQL, which consists of one or more database operations. These operations are connected and are considered as an indivisible sequence. They work on an "all or nothing" principle, meaning “either all the operations of a transaction succeed and are committed to the database, or they all fail and are rolled back, leaving the database in its original state.” The reliability and integrity of transactions are ensured by the ACID properties, which stand for Atomicity (all or nothing), Consistency (data integrity), Isolation (concurrent transactions don't interfere), and Durability (changes persist).
14) How can you secure your SQL queries against SQL injection attacks?
By preparing parameterized queries, SQL injection attacks can be avoided. Careful use of parameterized stored procedures in the database separates code from data, preventing malicious code execution.
15) Describe the concept of common table expressions (CTEs) and their benefits.
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are used in SQL to simplify complex queries and enhance code readability and maintainability. They improve modularity by allowing complex logic to be pre-defined and reused within the main query.
16) Describe the functionality of triggers in SQL and their different types.
Triggers are stored procedures that act on a table when given a response to specific events. Statements like INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE are some of the examples of triggers that are usually used. They can be used for enforcing business logic, data validation, or maintaining data consistency.
17) Explain the difference between full outer joins and full joins in SQL.
Both full outer joins and full joins return all rows from both tables. However, both of them work in a different sense: “a full outer join preserves NULL values in unmatched columns, while a full join may replace them with default values depending on the database engine.”
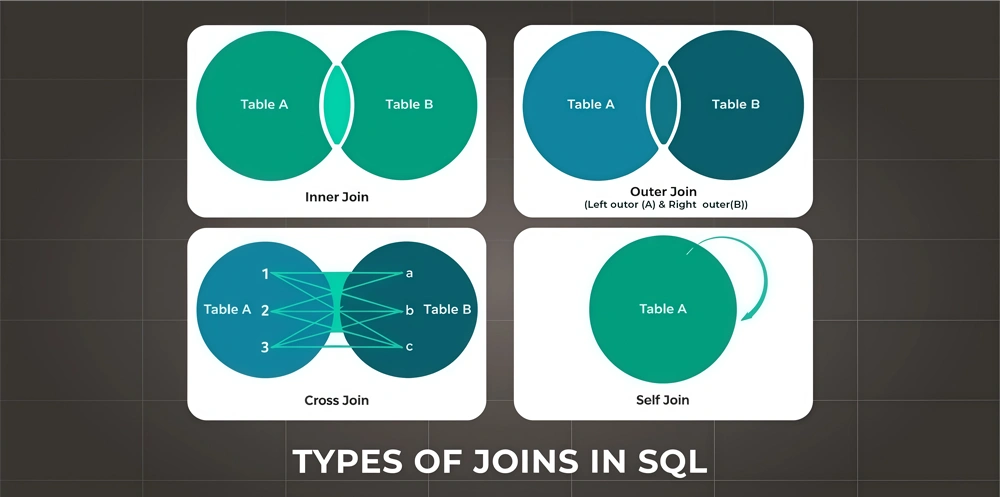
18) Describe the functionality of MERGE statements in SQL.
MERGE statements combine INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations into a single statement. With efficient data manipulation, this statement allows you to execute conditional actions based on existence or matching criteria.
19) Explain the concept of database partitioning and its benefits.
Database partitioning is used to divide a large table into smaller, manageable segments based on a chosen key. This way, the performance is improved as it allows queries to target specific partitions and reduces I/O operations.
20) Write a query to find the top 5 customers with the highest total order amounts.
SQL Code
SELECT CustomerID, SUM(OrderAmount) AS TotalOrderAmount
FROM Orders
GROUP BY CustomerID
ORDER BY TotalOrderAmount DESC
LIMIT 5;
Advanced Level (Query Based)
21) Write a query to find the manager for each employee in a company, even if the employee doesn't have a manager assigned.
SQL Code:
SELECT e.EmployeeID, m.ManagerName
FROM Employees e
LEFT JOIN Employees m ON e.ManagerID = m.EmployeeID;
22) Write a query to find the difference in days between the order date and the ship date for each order.
SQL Code:
SELECT OrderID, DATEDIFF(day, OrderDate, ShipDate) AS DaysDiff
FROM Orders;
23) Write a query to find the nth highest salary in an employee table.
SQL Code:
SELECT Salary
FROM Employees
WHERE Salary IN ( SELECT TOP 1 Salary
FROM ( SELECT Salary, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY Salary DESC) AS RowNum FROM Employees ) AS Subquery WHERE RowNum = n);
24) Write a query to pivot data from rows to columns, showing the total sales for each product category by month.
SQL Code:
SELECT Month,
SUM(CASE WHEN ProductCategory = 'Electronics' THEN Sales ELSE 0 END) AS Electronics,
SUM(CASE WHEN ProductCategory = 'Clothing' THEN Sales ELSE 0 END) AS Clothing,
... (add more categories)
FROM SalesData
GROUP BY Month;
25) Write a query to find the product categories with the highest and lowest total sales for the previous year.
SQL Code:
SELECT ProductCategory, SUM(SalesAmount) AS TotalSales
FROM SalesData
WHERE SaleDate >= DATEADD(year, -1, GETDATE())
GROUP BY ProductCategory
ORDER BY TotalSales DESC, TotalSales ASC
LIMIT 2;
26) Write a query to find the manager hierarchy for a specific employee, showing all levels up to the CEO.
SQL Code:
WITH ManagerHierarchy (EmployeeID, ManagerID, Level) AS (
SELECT EmployeeID, ManagerID, 1 AS Level
FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeID = <employee_id>
UNION ALL
SELECT e.EmployeeID, m.ManagerID, h.Level + 1
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN ManagerHierarchy h ON e.EmployeeID = h.ManagerID
INNER JOIN Employees m ON e.ManagerID = m.EmployeeID
WHERE m.ManagerID IS NOT NULL )
SELECT EmployeeID, ManagerID, Level
FROM ManagerHierarchy
ORDER BY Level DESC;
27) Write a query to find the total number of customers who placed orders in each quarter of the last year.
SQL Code:
SELECT DATEPART(quarter, OrderDate) AS Quarter, COUNT(DISTINCT CustomerID) AS Customers
FROM Orders
WHERE OrderDate >= DATEADD(year, -1, GETDATE())
GROUP BY DATEPART(quarter, OrderDate)
ORDER BY Quarter;
28) Write a query to find the department with the highest average salary for employees who have been with the company for more than 2 years.
SQL Code:
SELECT d.DepartmentName, AVG(e.Salary) AS AverageSalary
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN Departments d ON e.DepartmentID = d.DepartmentID
WHERE e.HireDate < DATEADD(year, -2, GETDATE())
GROUP BY d.DepartmentName
ORDER BY AverageSalary DESC
LIMIT 1;
29) Write a query to find employees who have never placed an order.
SQL Code:
SELECT e.EmployeeID, e.EmployeeName
FROM Employees e
LEFT JOIN Orders o ON e.EmployeeID = o.CustomerID
WHERE o.CustomerID IS
30) Write a query to find employees who earn more than the average salary in their department.
SQL Code:
SELECT e.EmployeeID, e.EmployeeName, d.DepartmentName, e.Salary
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN Departments d ON e.DepartmentID =
Tricky Interview Questions to Confuse Candidates
Here are a few questions, which will be presented to you based on the sample tables given below.
Customers Table:
|
Customer ID |
Name |
City |
|
1 |
John Levi |
New York |
|
2 |
Jane Tye |
Los Angeles |
|
3 |
Mike Foley |
Chicago |
|
4 |
Alice White |
New York |
Orders Table:
|
Order ID |
Customer ID |
Order Date |
Order Total |
|
100 |
1 |
2023-07-01 |
100.00 |
|
101 |
2 |
2023-06-15 |
50.00 |
|
102 |
3 |
2023-07-05 |
150.00 |
|
103 |
1 |
2023-07-07 |
75.00 |
|
104 |
4 |
2023-07-02 |
200.00 |
31) Find the customer who has placed the highest total order value.
SQL Code:
SELECT c.name, SUM(order_total) AS total_order_value
FROM Customers c
INNER JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY c.name
ORDER BY total_order_value DESC
LIMIT 1;
32) Find the average order value for each city.
SQL Code:
SELECT c.city, AVG(o.order_total) AS avg_order_value
FROM Customers c
INNER JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
GROUP BY c.city
33) Find the total number of orders placed by each customer, excluding orders placed in June.
SQL Code:
SELECT c.name, COUNT(*) AS num_orders
FROM Customers c
INNER JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE MONTH(order_date) <> 6
GROUP BY c.name
34) List all orders placed on specific dates (eg, 2023-07-04 and 2023-07-06) and their corresponding customer names.
SQL Code:
SELECT c.name, o.order_date, o.order_total
FROM Customers c
INNER JOIN Orders o ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id
WHERE order_date IN ('2023-07-04', '2023-07-06');
35) Find the month with the highest total order value.
SQL Code:
SELECT MONTH(order_date) AS order_month, SUM(order_total) AS total_order_value
FROM Orders
GROUP BY MONTH(order_date)
ORDER BY total_order_value DESC
LIMIT 1;
These are some of the top SQL questions that are generally asked at an interview by big firms. However, to do well in your upcoming interviews, you must practice the query code well and strengthen your basics, as anything can be asked there!
















