Expert Interviews
- University Reviews
- Career Guide
 Video Counseling
Video CounselingImportant Facts
- Ask any Question - CV Forum

Education System India Explained – New Edu Policy 2026
Priyanshu Bhatt Jan 21, 2026 63.4K Reads

India is among the traditionally rich countries in terms of imparting knowledge and education, with universities like Takshashila and Nalanda, the oldest university system in the world. Since then, the education system has evolved a lot in India. From Gurukuls to modern schools to online colleges, there have been some massive changes in the education system in India.
In this blog, we will discuss the evolution of the education system in India, from history to the present, and what lies in the future. We will also discuss the changes in the new National Education Policy (NEP) and how it plans to reform the current education system for a brighter future.
Education Policy In India- Facts & Statistics
The education system in India has undergone a significant change, especially with the advent of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. The emphasis has been shifted towards holistic, flexible, and multidisciplinary education that is consistent with the 21st-century goals. Check out these newest facts, statistics, and highlights of India’s education policy today in the year 2026.
- NEP 2026 proposes extending free and compulsory education to the age group 3–18, but legally, RTE still applies to ages 6–14
- India's population has crossed 1.43 billion, with over 25% under the age of 15, highlighting the critical need for robust primary and secondary education infrastructure.
- The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education rose to 32.5% in 2026, as per the latest AISHE report, with a goal to hit 50% by 2035.
- Adult literacy rate (15+ years) is now estimated at 77.2%, with male literacy at 84.7% and female literacy improving to 69.4%.
- Kerala continues to lead with a literacy rate exceeding 96%, followed by states like Himachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
- The University of Delhi, IIT Bombay, and IISc Bangalore remain among the top higher education institutions in India.
- India now ranks 27th in the 2026 English Proficiency Index, showcasing steady improvement in global communication skills.
Future Goals of the Indian Education System
India is a growing industry in the educational sector and has set various milestones in the upcoming years. India has been an active participant in the UN’s E9 Initiative, focusing on digital learning and bridging educational inequalities, especially for girls. The Union Budget 2025-26 allocated:
- ₹1.24 lakh crore to education, ₹73,000 crore for school education, and ₹51,000 crore for higher education.
- A significant push has been made for digital infrastructure, teacher training, and research & innovation.
- India is also working towards the ambitious goal of having 25 Indian universities among the global top 200 by 2030, and becoming a top 5 R&D nation, with projected annual R&D spending of $140 billion.
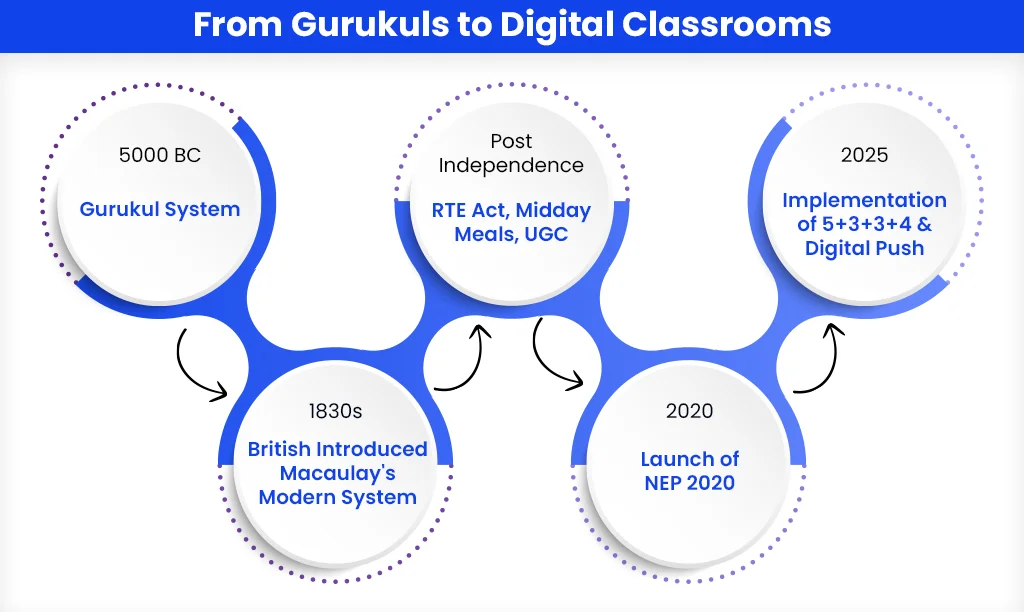
History of the Education System In India
Traditionally, education in the Indian subcontinent was mostly for the upper-caste. But over time, it became a right for all, regardless of caste, class, or other differences.
The ‘Gurukula’ system, dating back to 5000 BC, was India’s first education model. A student (shishya) would approach a teacher (Guru) for admission. If accepted, the student stayed at the Guru’s home, helped with chores, and built an emotional bond.
The Guru taught science and math along with Philosophy and Metaphysics. Sanskrit was the medium. The focus was on practical learning, nature, and real-life situations, aiming for students’ overall development, cognitive, mental, physical, and spiritual.
Rather than rote learning, the focus was on human values, empathy, self-reliance, creativity, morals, and ethics, so students could apply knowledge to real-world problems.
This system was replaced in 1830 by the modern school system introduced by Lord Macaulay. It brought classroom learning, cut emotional teacher-student bonds, and stressed Science and Math while ignoring Philosophy, Ethics, etc. English became the medium.
This system evolved and still exists. But the old 10+2 structure was recently replaced by the 5+3+3+4 system, with changes like equal focus on theory and practice, multidisciplinary choices, and digital learning.
Key Highlights of the New Education Policy (NEP) 2020
The school board examinations will encourage knowledge and application-based learning.
The school curriculum will be focused more on core concepts, and the pedagogy will introduce more practical learning:
- The 10+2 school system will be replaced by the 5+3+3+4 school system.
- Introduction of vocational education from the 6th grade.
- Except for the medical and law colleges, all the other higher education institutions will be governed by a single umbrella body, and the same set of regulatory norms, academic standards, and accreditations will be set in place for both private and public higher education institutions.
- Higher education will be multidisciplinary, with the aim for all universities to become multidisciplinary by 2040.
- There will be multiple exit options in the undergraduate degree, which means that if a student exits the UG course after 1 year, they will get a certificate, if they exit after 2 years, they will get a diploma, and they will get the degree after completion of 3/4 years.
Essential Reforms in the New Policy for School Education
The following are some of the important points included in the new policy for school education
- All levels of school education will be singularly regulated
- There will be a new and revised curriculum for the early childhood care and education
- The school curriculum and the pedagogy of teaching will be reformed towards being more progressive and focused on the overall development of students.
- Apart from Hindi and English, the medium of instruction will be in regional/local languages up to class 5th or 8th to promote regional languages.
- The new assessment system will be more competency-based rather than just theory-based.
- There will be some changes in the recruitment process of teachers as it will become more transparent. The promotions will also be based on merit henceforth.
Online Education System In India
The Government of India, in the new National Education Policy (NEP) 202,0 has laid a lot of emphasis on online education as new circumstances require new and evolved initiatives. The recent pandemic and the rise in epidemics have made the necessity of online education very clear.
The government has directed education institutions to leverage the benefits of technology but acknowledging the potential risks at the same as well. The government has asked the existing digital online platforms along with ICT-based educational initiatives to optimise and expand to meet the present and future challenges in offering quality education.
The reason why even the government has been focusing on promoting online education is because of the many advantages that accompany it. It is time that we move on from the age-old traditional education system brought by Macaulay.
Online education sort of breaks stereotypes of the 6 hour long classroom education system. Online education focuses more on the practicality of the learnings received by the students. The emphasis is on acquiring skills rather than just memorising what is written in the books.
The following are the advantages of the online education system in India and how it is important and prevalent in the current times:
- Flexibility
- Affordability
- Diverse Options
- LMS
- Time Management

Some Of The Best Online Universities In India
Online education in India has touched greater heights in the dynamic realm of education. However, one of the major concerns regarding online education is the validity and worth of online education. Let us tell you that online education and distance education is valid and approved by UGC in India, but one thing that you need to keep in mind is that the university you are applying to has the necessary approvals and accreditations.
Below are some of the major online institutes in India from where you can pursue quality education while getting the highest return on your investment. However, there are quite more, but for now, check out these best in industry online institutes:
|
Some of the Best Online Universities |
||
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
NEP stands for the National Education Policy. This policy is drafted by the Ministry of Education (MoE), Govt. of India. The policy mentions and describes all the norms, rules, regulations, and guidelines regarding education in India at all levels.
Some major changes according to the new education policy, the 10+2 school education system will be replaced by the 5+3+3+4 system. The policy also has emphasised on the promotion of online as well as open and distance education.
In higher education, there will be an exit policy which will allow students to exit from a degree course at any point in time with a certificate if exit is after 1 year, a diploma after 2 years, and a degree after 3/4 years.
The new structure divides schooling into four stages:
- Foundational (5 years): Ages 3–8 (including pre-school)
- Preparatory (3 years): Ages 8–11
- Middle (3 years): Ages 11–14
- Secondary (4 years): Ages 14–18
- This aims to align education with cognitive development stages.
NEP 2020 supports the integration of technology in education by promoting digital infrastructure, online learning platforms, and virtual labs. It also aims to bridge the digital divide and improve access to quality education across rural and urban areas.
Yes, online education is valid and approved by the University Grants Commission (UGC). However, it is important to ensure that the university offering the program has proper UGC-DEB approval and relevant accreditations.
The NEP 2020 promotes the use of mother tongue/regional language as the medium of instruction till at least Grade 5, and preferably till Grade 8, to strengthen foundational literacy and cognitive development.
As of 2024, India’s Gross Enrolment Ratio in higher education is 32.5%. The NEP aims to increase this to 50% by 2035.
India aims to have 25 universities ranked in the global top 200 by 2030 and become a top 5 R&D nation. The policy also focuses on promoting multidisciplinary learning, vocational education, and skill-based training.

3 Years of Experience | Content Specialist I Copywriter
Writing what Google loves, and students need.
Every query is essential.
Our team of experts, or experienced individuals, will answer it within 24 hours.
Recommended for you
Tired of dealing with call centers!
Get a professional advisor for Career!
LIFETIME FREE
Rs.1499(Exclusive offer for today)

Pooja
MBA 7 yrs exp

Sarthak
M.Com 4 yrs exp

Kapil Gupta
MCA 5 yrs exp
or



Career Finder
(Career Suitability Test)
Explore and Find out your Most Suitable Career Path. Get Started with our Career Finder Tool Now!
ROI Calculator
Find out the expected salary, costs, and ROI of your chosen online university with our free calculator.
