Expert Interviews
- University Reviews
- Career Guide
 Video Counseling
Video CounselingImportant Facts
- Ask any Question - CV Forum

What is Intellectual Property Law? Types & Importance
Sonika Jul 21, 2025 1.1K Reads

Intellectual property is such a property that we can consider as a thought, idea, or any creation that has some value in the market or can be an asset shortly. Such creations can involve symbols, music tracks, names, images, artistic work, design, and inventions. Similar to physical assets, these can also considered assets and can be owned, licensed, or inherited.
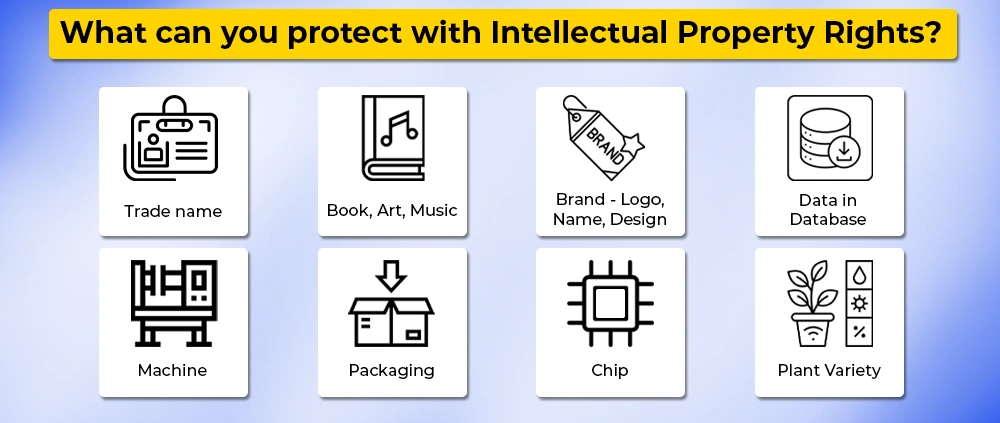
Intellectual Property Law
Intellectual property law is such a law through which one can protect Intellectual property and the owner or the creator has the rights over the use of their work. The owner can claim that it's his work and can control unauthorized work. In general. This law promotes innovation and creativity by offering benefits to the owners.
Well, Intellectual property has its importance in that it encourages other inventors and creators so that they can invent new things and create new art pieces. Let’s see it through an example, just imagine that there is a certain law that can protect your idea, then only you can invest money and time in creating or inventing something. In a similar way, if a company gets protection over their idea on the new product, services, or content, then why won’t they sweat their guts out?
They will try their best to offer the best to their audience or customers. Additionally, IP rights allow the creator to benefit financially from their product or creation. In such a manner, IP laws do not only protect the interest of the creator but also serve the people in whatever way they can. Remember, this is a competitive world, you need to think differently and take the help of the laws provided to the public as it work on - a first come, first serve.
Why is intellectual property important?
- Protects Creative Works: It prevents unauthorized use of any creator’s work which has been protected by copyright or Intellectual property right.
- Enhances Competitive Advantage: Trademarks and patents provide companies with a stand out in the market and increase their market share.
- Promotes Knowledge Sharing: after getting the content or invention prevented by the Intellectual Property right, creators or inventors openly share their ideas and creations with the public.
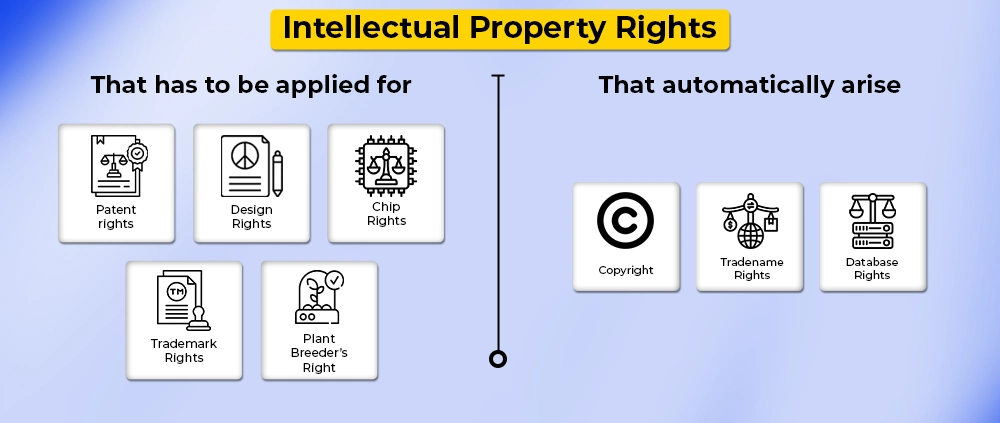
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
There are various types of Intellectual Property Rights, that support each idea, innovation, new product, or service and give them the security to not be used unauthorized by any other individual. Let’s learn about the main types of Intellectual Property Rights.
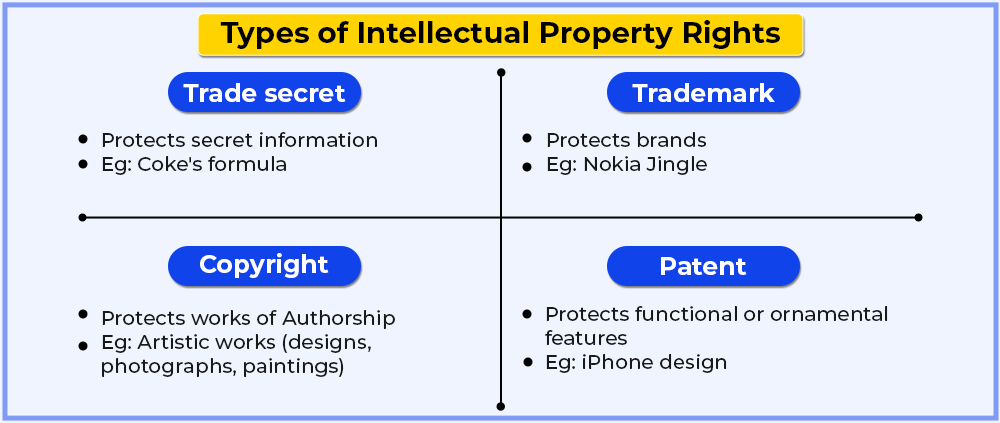
Patent
A patent is a right of an inventor over their invented product, idea, or service which must be useful for the people living in this world. This right prevents other people from making, selling, using, or distributing it without the permission of the inventor. To get a patent over the invention, it must be novel, non-obvious, and industry-applicable.
To get a patent over any new product or service, there are certain sets of rules that one must follow:
- The product, invention, or service must be novel which means it must be something new. It did not exist in the market before the idea If filed to get the patent.
- Only ideas can not be patented; you must submit the details of that idea and how it will help in the economic growth of the country.
- After the expiry date of the patented invention, anyone can sell it, use it, and manufacture it. After the patent expires, it enters the public domain which means, now, there is no authority of the inventor and can be used by anyone.
*The term of a patent is 20 years from the date of filing the patent application, not from the patent is granted. Also, if you wish to stay longer, you need to pay a certain annual renewal fee.Get more information on the process and other details regarding the Patent-https://ipindia.gov.in/writereaddata/Portal/News/758_1_Patents__Amendment__Rules__2021.pdf
Trademark
A trademark is a design, sign, phrase, word, logo, or a combination of any of these, which helps any product or service to be distinguished from the product or service offered by any other party. Let’s see it through examples: what can be trademarked?
- Words and names (Adobe, Coca-Cola)
- Sounds (Nokia Jingle)
- Slogans (McDonald's - I’m loving it)
- Color (Associated with brands, it’s quite hard to get trademarked)
- Logos and symbols (New Balance, New Me, Lacoste)
*These trademarks must be taken over such things that cannot be generic or descriptive of the product (like Shoes for footwear). There are certain rules. Generally, a trademark is valid for 10 years from the date of filing. You can renew it if you can pay a prescribed renewal fee till you want it to be trademarked.
Here is the link, where you get all the information, rules, and regulations that are developed for getting a trademark - https://ipindia.gov.in/writereaddata/Portal/News/758_1_Patents__Amendment__Rules__2021.pdf
Copyight
Copyright is a kind of protection shield provided to the original artistic work, musical work, literary work, and dramatic works. These may include paintings, software, songs, tracks, films, and more. It cannot directly protect the idea, but can protect the way it is expressed.
Let’s see it clearly with the help of a few examples:
- Artistic works (designs, photographs, paintings, drawings, sketches)
- Cinematographic films (Biopics, documentaries, movies)
- Computer software (code and user interface)
- Musical works (composition with or without lyrics)
- Sound recordings (songs, tracks, podcasts)
- Literary work
- Dramatic work
Here, you can check all the terms and conditions on the copyright - https://ipindia.gov.in/writereaddata/Portal/News/312_1_TRADE_MARKS_RULES_2017__English.pdf
Trade secrets
A trade secret must be kept secret from the people and other businesses. This is something that should remain confidential and which is not known to the public. It can be anything like the recipe, formula, design, composition of medical drugs, methods, formula, and more.
Well, here is a difference between trade secrets and patent or copyrights which is that no government body is involved. The confidentiality or the protection of the details of any product depends on the owner’s efforts to keep them safe and confidential from other parties that are standing in the competition and running their business side by side.
Let’s look at a few examples of Trade Secrets to understand more about it:
- A startup’s business model or product roadmap
- KFC’s Spice Blend
- Google’s search algorithm
- The formula of Coca-Cola
- Stuffing of any food item
Here is the link to get detailed information regarding the trade secrets - https://www.wipo.int/documents/d/trade-secrets/docs-overview-country-sheets-india-final.pdf
How does this law work in real life?
Intellectual Property is one of the powerful tools that protects what’s yours. It may involve innovations, branding, and creation. Let’s learn how it works in real life, in brief:
- Protection through legal rights
- Safeguards traditional knowledge
- Commercial use and licensing
- Tech companies protect algorithms
- Enforcement and legal actions
- Prevent being copied in the market

- Support e-commerce
- Encouraging business growth
- Encourages R&D in Pharmaceuticals
- Global reach
- Boost Global Reaches franchising
- Startups attract funding using IP
- Authors and artists earn Royalties
Steps for creators, startups, and professionals
1. Identify IP Assets:
Start with something new in the market as it should be novel means that does not exist before. Create something that has value and is original.
2. Choose the right IP type:
- It can be patents
- It can be trademarks
- It can be copyright
- It can be trade secret
3. Protect the IP legally:
First, remember to file for registration with some relevant authority (for patents and trademarks - IPO in India)
4. Do not forget to keep proper documentation:
- Maintain the records, drafts, and records of the creation date
- Keep the signed contracts and licensing documents safe somewhere
5. Keep an eye on your product:
- - For some infringement
- - If someone is not using it without your permission
6. Monetize your IP
Key facts and authorities: IP Law in India
Here is a quick detail on the key facts and authorities related to the IP Law in India:
Legal framework
You must use the legal way to get your patent or use proper IP laws
- The Copyright Act. 1957 (amended in 2012)
- The Trade Marks Act, 1999
- The Patent Act, 1970 (amended in 2005)
- The Designs Act, 2000
- The Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Design Act, 2000
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999
- The Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001
Additionally, India is a signatory to International treaties, including the following:
- Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT)
- TRIPS Agreement (WTO)
- Madrid Protocol (for international trademark protection)
- Berne Convention
Governing bodies
For IP administration in India, the government authority responsible is the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trade Marks (CGPDTM) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT))
Let’s know about the key offices under CGPDTM:
- Trademark Registry (main office in Mumbai, branches in other metros)
- Copyright Office (New Delhi, under Ministry of Education)
- Patent Office (Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata)
- Geographical Indications Registry (Chennai)
- Design Office (Kolkata)
- Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority (New Delhi)
|
Recent Developments in Indian IP Law |
|
|
Digital Copyright Enforcement |
Startup IP Support: The Startup India Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) |
|
E-filing and Automation |
IPR Awareness Programs |
|
Increased International Cooperation |
Geographical Indications (GI) Tag Promotions |
*To know more about these you can visit the official website of the Indian Patent Laws - https://ipindia.gov.in/
Universities offering LLM in Intellectual property Law
Various universities in India offer law degrees in Intellectual Property Law. A few of the top universities are listed below in the Table format:
|
Universities offering LLM in Intellectual Property Law |
|
|
Jindal Global School of Law |
Symbiosis Law |
|
Amity Law School, Noida |
Lovely Professional University (LPU) |
|
National Law University Delhi (NLUD) |
Nalsar University of Law |
|
School of Las, UPES |
GNLU Gandhinagar (NLU) |
|
Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University |
Aligarh Muslim University |
Jindal Global Law School (Blended Learning Program)
Jindal Global Law School offers students an LLM program (1-year program) in a blended learning mode. Here you can complete this program in only one year. However, the university offers an additional 2-3 years to complete the degree. Here, you get all the study material about the specialization of their Learning Management System (LMS) which includes live sessions, recorded lectures, case studies, assessments, and more things. You also get to learn from their e-library, which is accessible 24x7.
Specialization offered:
- Corporate & Financial Law
- AI and Emerging Technologies
- Intellectual Property & Technology Law
- Dispute Resolution
- Taxation Law, Policy and Regulation
Eligibility criteria:
- Candidate must have passed an LLB program (3-year or 5-year) with minimum qualifying marks
- Students must have a scorecard of any of the entrance exams (LSAT, CLAT PG, or DU LLM - any of these).
- Additionally, candidates who have a valid international LSAT score within five years of applying will not be required to take the JSAT.
Fee structure:
Course fee - INR 3,50,000
|
Specialization |
Subjects |
|
Intellectual Property & Technology Law |
|
Conclusion
This blog was all about Intellectual property rights and Intellectual Property Laws. In this blog, you get to know about how IP laws work and the rules that are implemented on the products, ideas, services, or inventions produced by an individual. Also, according to the WIPO report: India Emerges as a Global IP Leader In 2024 that’s something good for India. Indian IP laws are well-established and one can rely on them but they also need to keep their eyes open, if anybody is using your patented technique or anything else without your permission then you can sue them on the grounds of infringement.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
If you work on your product or any new creation from the ground and do not take the ideas of others, then you can avoid copyright infringement as you have not copied any other’s idea.
The right to a patent belongs to the inventor of a product, concept, or service that must benefit the world's population. Without the inventor's consent, others are prohibited from producing, distributing, selling, or utilizing it. The innovation must be new, non-obvious, and applicable to the industry to be granted a patent.
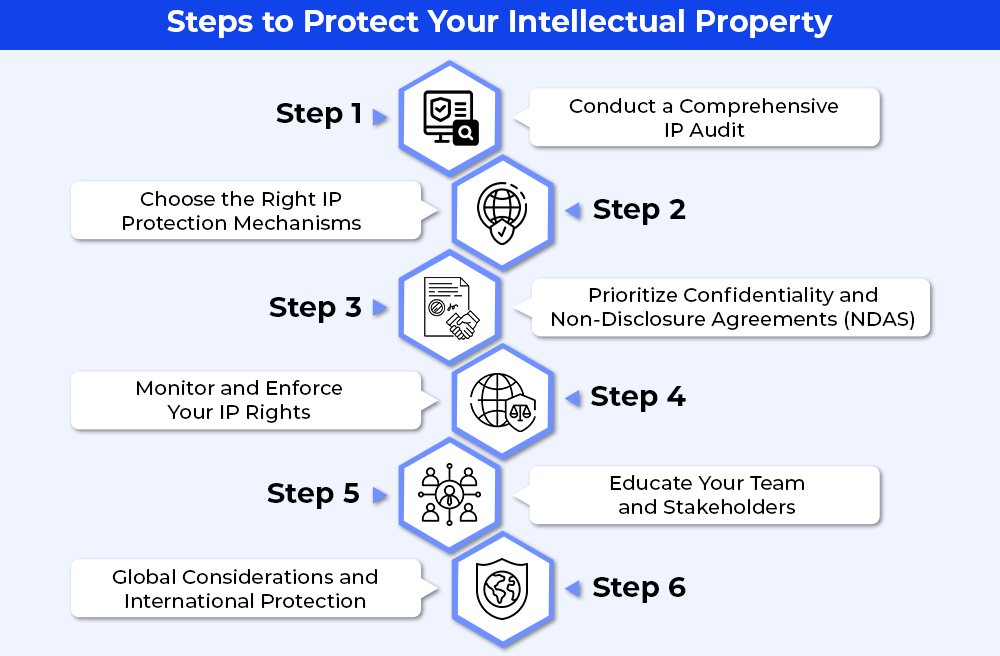
Here are a few points that you need to consider as the steps to follow to keep your Intellectual Property safe:
- Conduct a Comprehensive IP Audit
- Choose the Right IP Protection Mechanisms
- Prioritize Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAS)
- Monitor and Enforce Your IP Rights
- Educate Your Team and Stakeholders
- Global Considerations and International Protection
The value of intellectual property lies in its ability to encourage other creators and inventors to produce new works of art and invention. Let's take an example. Suppose that a law exists that protects your concept. In that case, only you would be able to spend time and money developing or producing something.
Here are all 4 types of Intellectual Property:
- Patents
- Trademarks
- Copyrights
- Trade secrets
IP stands for Intellectual Property. It is referred to as a creation that can be anything but it must be novel, non-obvious, and industry-applicable. For example, Artistic works (designs, photographs, paintings, drawings, sketches), Cinematographic films (Biopics, documentaries, movies), Computer software (codes and user interface), Musical works (composition with or without lyrics), Sound recordings (songs, tracks, podcasts), Literary work, Dramatic work, and more.
From the date of filing a patent, one can get 20 years of patent. If that individual wishes to keep that product to b patented for a longer period, then he must ensure that he is paying the prescribed annual fee.
The term infringement is used for any sort of violation or breaching of the rules, or any unauthorized act.
To be eligible for IP law, one must have completed at least an LLB or equivalent degree from a recognized university. Additionally, after completing any bachelor’s program, you can enroll in the programs that are specifically designed to help you become an IP specialist in that particular field or subject. For example, in India, IIPTA (Indian Institute of Patent and Trademark Attorney) offers you learning programs that can help you to be in this field.

By Sonika
3 Years of experience/ academic writer/ freelance writer
An academic writing expert with an experience of 4 years.
Every query is essential.
Our team of experts, or experienced individuals, will answer it within 24 hours.
Recommended for you
Tired of dealing with call centers!
Get a professional advisor for Career!
LIFETIME FREE
Rs.1499(Exclusive offer for today)

Pooja
MBA 7 yrs exp

Sarthak
M.Com 4 yrs exp

Kapil Gupta
MCA 5 yrs exp
or



Career Finder
(Career Suitability Test)
Explore and Find out your Most Suitable Career Path. Get Started with our Career Finder Tool Now!
ROI Calculator
Find out the expected salary, costs, and ROI of your chosen online university with our free calculator.
