The terms “artificial intelligence” and “machine learning” are not only used synonymously in many cases by technology enthusiasts and learners but are also confused as technological concepts in application. While machine learning and artificial intelligence are indeed closely related in terms of their foundations and uses, there are certain key distinctions between these two concepts and their applications.
If you are also a technology enthusiast interested in understanding the distinctions between AI and ML, then continue reading to find out their key differences as well as similarities between these areas and explore their applications and implications.
What are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)?
Artificial intelligence in essence is a domain of technology that is concerned with the creation of machines, softwares and computer programs capable of simulating human intelligence in their functioning in terms of decision-making, problem-solving, operations, conversational patterns and so on.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thus, it can be conceptualised as a set of systems that support the operations of machines/softwares in manners similar to the cognitive functions performed by humans. It incorporates a wide range of technologies and systems that allow it to perform functions efficiently in a smart manner.
On the other hand, machine learning (a subfield of AI) is the branch of computer science that is concerned with the creation of models that can analyse vast amounts of data to autonomously learn and improve its functioning by identification of patterns and information. Machine learning involves the use of algorithms that allow for the analysis of large amounts of data to draw relevant insights and further guide decisions and problem-solving.
Similarities between AI and ML
Before diving into the ways in which artificial intelligence and machine learning differ from one another, here are a few similarities between these domains as explained below.
1 ) Subfields in Computer Science
Both AI and ML are areas within the domain of computer science that focus on softwares capable of handling complex data and information and accordingly performing operations on them. There is also an emphasis laid on effective learning by these softwares in both the domains of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
2 ) Simulation of Human Problem-Solving
Another major similarity between artificial intelligence and machine learning is that both these domains are focused upon the creation of systems (be it softwares or models) that can mimic human cognitive functioning and intelligence and perform operations including decision-making and problem-solving similar to humans. AI and ML both lay emphasis on learning by machines and softwares to trace data patterns and draw insights from them to make effective decisions and solve problems.
3 ) Wide Applications
Another similarity of artificial intelligence and machine learning revolves around their applications across a wide variety of fields expanding beyond computer sciences. Not only are AI and ML technologies interdisciplinary in nature, they both have implications for fields ranging from healthcare, finance, education, advertising to medicine, engineering, scientific breakthroughs and so on.
4 ) Similar Underlying Components of Technology
Since ML is a subdomain of AI, they both understandably are based on similar underlying components of technology, including the heavy dependence on data, pattern recognition, continuous learning and so on. They both implement complex models and algorithms to identify patterns of data and further use them for driving decisions and performing operations.
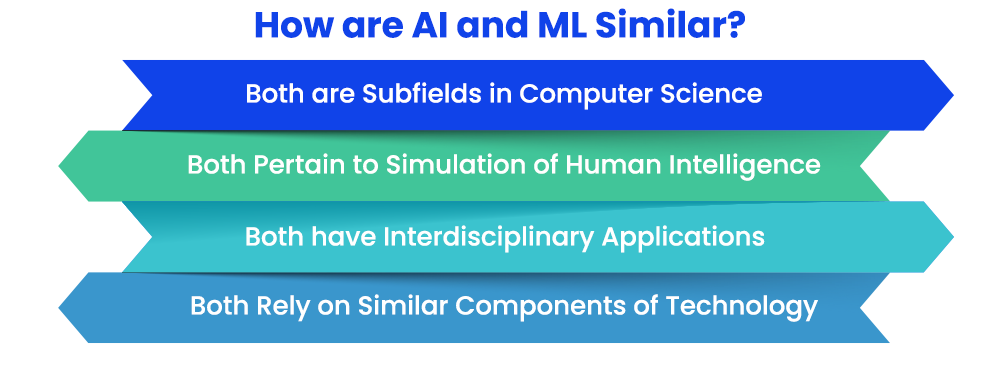
Thus, as can be seen, artificial intelligence and machine learning originate from similar underlying concepts of computer science and utilise an interdisciplinary approach to track and simulate operations and problem-solving similar to human intelligence.
Differentiating between AI and ML
However, despite having similar bases of technology, artificial intelligence and machine learning are distinct fields that have certain key differences between them. Herein, we have delineated the major differences between artificial intelligence and machine learning, ranging from their historical development to their working and underlying processes of implementation. 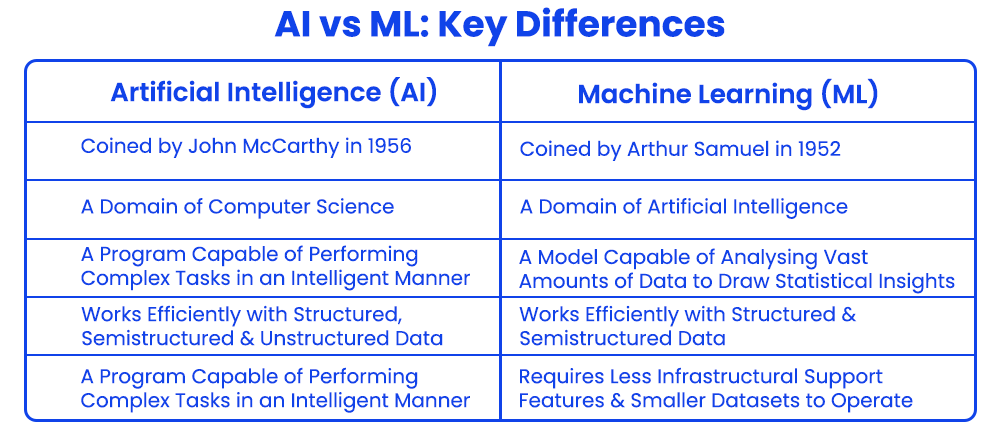
1 ) History of Development and Coinage
To begin with, knowing the difference in the historical development of the concept of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning is important.
Artificial Intelligence as a term was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956, and was also introduced in an international conference at Dartmouth College.
On the other hand, while the concept of active learning by machines has been stated and described by thinkers, theorists and scientists, it was first introduced in 1952 by Arthur Samuel. Despite the coinage of the term, “self-teaching computers” was used as a term to describe ML technologies and models.
2 ) Categories to which they Belong
While both artificial intelligence and machine learning belong to the category of computer science, artificial intelligence describes a broad category of technologies, softwares and computer programs aimed at simulating the patterns of human intelligence. On the other hand, machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, i.e. it includes machine models which can autonomously learn and integrate vast amounts of data to guide better decision-making and problem-solving.
3 ) Main Objectives and Purposes of Use
While both AI and ML aim at enhancing the performance of machines and computer programs to reflect human intelligence, the purpose and objectives of artificial intelligence and machine learning are distinct.
Artificial intelligence systems are created with the aim of developing complex and holistic systems, usually including computer softwares and programs that can effectively simulate human intelligence and cognitive capabilities to perform tasks and solve complex problems including learning, pattern-recognition, calculation, programming and so on. The major focus of developing AI is to create a system capable of successfully completing complex tasks with intelligence.
On the other hand, the primary focus of machine learning models is to analyse vast amounts of data and further draw insights from them and learn from the insights. Thus, machine learning involves utilising statistical models to analyse vast data and further find results with a given degree of confidence (which indicates the probability of accuracy of the findings). As can be seen, the major focus of machine learning is accuracy of findings. AI moves beyond the data analysis of machine learning to further integrate the findings into systems to solve problems accurately in the future.
4 ) Key Methods Used for Implementation
When it comes to the various methods implemented in artificial intelligence and machine learning, the two domains involve distinct technologies to run their basic operations.
Artificial intelligence models and softwares utilise a number of technologies to sustain and operate effectively, including the likes of machine learning, deep learning, neural networks (including convoluted neural networks, deep neural networks), generative AI, rule-based systems, genetic algorithms, search algorithms etc.
When it comes to machine learning, two major technologies underlie its operation–supervised learning and unsupervised learning. While supervised learning includes analysis of data clearly labelled as input to produce data insights labelled outputs, unsupervised learning is an exploratory approach wherein the ML model actively explores unlabelled data to draw new and undiscovered insights. Furthermore, in recent years, reinforcement learning involving the training of a machine learning model to arrive at optimal rather than simply accurate solutions, is also being implemented. ML usually makes use of technologies including (but not limited to) general adaptive networks (GANs), deep neural networks, statistical models including regression etc.
5 ) Process of Implementation
The process of developing and implementing AI and ML models are quite distinct from one another as well, with each involving different stages of creation of the model before it can be integrated with other technologies.
In the case of artificial intelligence, the process of implementation passes generally through stages of problem identification, problem definition, data collection and preparation, data preprocessing, selection of a model, training of the model, evaluation and deployment, progress evaluation and debugging to enhance functioning.
On the other hand, the development and implementation of machine learning involves the selection of a meaningful dataset and feeding it into an ML model. Further, it involves the selection of a strategy for data analysis. Commonly used statistical strategies include linear regression, logistic regression, decision-tree analysis etc. Further processes include data refinement for error checking and enhancing the effectiveness of the ML model.
6 ) Minimum Requirements for Implementation
The infrastructural and data requirements for AI and ML systems also vary, with artificially intelligent systems requiring significantly more infrastructural support features than machine learning models.
On an average, varying with the particular operation that an AI model is designed to perform, it may require a large number of servers and machines working in tandem or simultaneously. For instance, a few complex AI models require about thousands of machines operating simultaneously in order to perform tasks.
On the other hand, machine learning models usually require a lesser number of data points and infrastructural support features. Dataset samples consisting of about a few hundred data points can also be used to train ML models. Moreover, depending upon the complexity of the operations and data analytical model chosen, a single server to a few server clusters are sufficient to run data analysis.
7 ) Types of Data Needed for Use
While artificial intelligence models and programs are designed to work efficiently with structured, semistructured and unstructured data, machine learning primarily works efficiently with structured and semistructured data. ML models which can work efficiently with unstructured data are still in the process of development.
The differences between artificial intelligence and machine learning can be summarised as tabulated below.
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
Machine Learning (ML) |
|
Artificial intelligence as a term was coined by John McCarthy in 1956. |
Machine learning was coined as a term by Arthur Samuel in 1952. |
|
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to any computerised system or program capable of performing complex tasks in an intelligent manner like humans. |
Machine learning (ML) refers to the ability of machines or computer programs to autonomously learn by analysing datasets. |
|
Artificial intelligence is a domain of computer science. |
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence. |
|
The main purpose of an AI system is to create a holistic system capable of performing complex tasks and solving problems. |
The main purpose of a machine learning (ML) system is to create a model that is capable of autonomous learning and accurate prediction. |
|
It uses technologies like machine learning, deep learning, neural networks, generative AI, rule-based systems, genetic algorithms, search algorithms etc. |
Machine learning uses technologies such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning. |
|
It includes stages like problem identification, problem definition, data collection and preparation, data preprocessing, model selection, model training, evaluation and deployment, progress evaluation and debugging. |
It includes stages such as selection of datasets, selection of statistical models, data refinement for error checking and so on. |
|
It usually requires greater infrastructural support and datasets often involving hundreds of server clusters. |
It requires comparatively less infrastructural support and datasets, ranging from a few server clusters and datasets of nearly 100 data points. |
|
Artificial intelligence systems can function efficiently with structured, unstructured and semistructured data. |
Machine learning systems can function efficiently with structured and semistructured data. |
Integrated Use of AI & ML: Prospects and Benefits
To understand how AI and ML can be integrated, one must identify that boththat machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, meaning it can be utilised in tandem with the broader technology of AI to drive innovation.
As a result, machine learning technologies and models can be integrated in wider AI systems and softwares to enhance their accuracy and autonomous learning without the need for manual programming. The benefits of utilising ML models in AI softwares and programs include enhanced accuracy of the decisions made and problems solved by the model, autonomous learning by the model without the need for programming and ability to draw meaningful insights from vast amounts of data. The integrated use of AI and ML holds meaningful and bright prospects for the advancement of the fields as well as advanced application in other disciplines and services.
Applications of AI and ML Today
The applications of AI and ML technologies are becoming wider and diversified with time, with the integration in crucial fields such as medicine, healthcare, scientific discoveries, coding etc. taking centre-stage. AI and ML has found its applications and uses in a wide variety of domains ranging from everyday services to crucial industries.
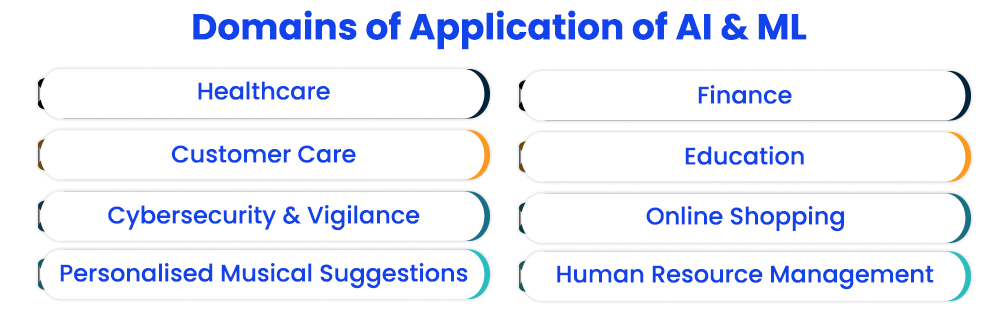
Mentioned below are a few of the significant domains of applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- AI and ML in Cybersecurity & Vigilance: AI-powered facial detectors, recognition softwares, motion detectors etc. have been widely deployed for the purpose of automated cybersecurity and cyber-vigilance in defence and other spheres.
- AI and ML in Education: AI-powered electronic learning tools, systems, self-study softwares, guided learning platforms, simulated learning platforms etc. are technologies that have become integrated into mainstream education services in the recent past. They hold the potential to transform how students learn and develop their skills and knowledge.
- AI & ML in Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, AI and ML technologies have been deployed in fields such as feedback tools for health management, AI-powered personalised reminders for healthcare, personalised virtual assistants for health management, appointment planners and so on. Some applications also include the integration of AI models in diagnosis and detection tools to identify data and accordingly provide potential diagnoses to patients’ tests.
- AI & ML in Financial Sectors: Whether it be the AI powered fraud detection applications, financial threat prediction softwares, loan approval predictors, e-payment applications or customer support for banking and BFSI sectors, the advancements being made in the field are significant.
- AI & ML in Customer Services: A major arena wherein the applications of AI and ML have transformed operations is customer services. With AI-powered chatbots and platforms for round-the-clock services to clients, the domain of customer services has expanded and majorly transformed with the integration of artificially intelligent models and platforms.
In addition to the aforementioned applications of AI and ML, their contributions to our daily life and functioning are surmount and often under-recognised. Ranging from online shopping applications to music applications providing personalised song suggestions, AI models have a role to play in enhancing services and user experiences.
Conclusion
Thus, although rooted in the same domain of computer science, artificial intelligence and machine learning differ in certain key domains with respect to their underlying components, purpose and functionality. However, when integratedly used, they hold immense potential for altering the face of computerised services, virtual assistance and automation.
Trending articles
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
















