With companies and business firms becoming increasingly aware of the potential to harness data insights to drive bottom-line profits, data science as a career has gained significant popularity as being lucrative and prosperous for growth opportunities in the past few years. Pursuing data science as a career is not only deemed prestigious but is also considered to provide diverse domains within it and climb the professional ladder as a tech-professional.
Consequently, many students and tech-enthusiasts may find themselves attracted to the field for professional opportunities but may not have the right career guidance to become a data scientist. In this blog, we have tapped into the variety of aspects related to becoming a data scientist, starting off right from the steps one can take to practise a data scientist to the core job responsibilities and skills of a data scientist needed to thrive in the field.
Continue reading to explore the career pathway to follow to become a data scientist and indulge in the intellectually stimulating and handsomely compensated profession!
What is Data Science?
Data science is a multidisciplinary function that focuses on the analysis of vast amounts of data to analyse them, draw meaningful conclusions from them and drive business decisions. Data science as a field of technology derives from the principles of mathematics, statistics, probability, artificial intelligence, computer engineering, and database management.
While earlier conceptualisations of data science often equated it with statistical principles, in the current decade, the usage of the term has been refined and specified to indicate the practice of analysing big data to draw business-driven insights, thus bringing focus to the need for finding meaningful patterns in large amounts of raw data from a business-driven orientation. Data science utilises statistical and predictive analyses to create predictive models and draw data insights.
What Does a Data Scientist Do: the Key Job Responsibilities of a Data Scientist
The job role of a data scientist, while being challenging, also provides scope for intellectual stimulation and using analytical skills to derive insightful conclusions about data. The job role of data science involves certain core job roles and responsibilities, a few of which have been summarised herein. Explore these job roles to analyse if the job description of a data scientist meets your career needs and skills and interests.
- Working with Large Datasets: This is the all-encompassing job responsibility of a data scientist. Data scientist job roles revolve around managing vast datasets and utilising the data with respect to its processing, mining, cleaning, interpretation and visualisation. If you have an acumen for managing and handling large amounts of data, then the role of a data scientist would not be overwhelming for you as a professional, however, if you lack the skills or enthusiasm for handling vast data on a regular basis, the career domain of data science may not be the most suitable field for your professional needs.
- Identifying Appropriate Datasets for Research: Before a data scientist engages in data processing and further analysis, the foremost responsibility is to identify the datasets which can be appropriately used for the purpose of drawing insights relevant to the organisation. For this, the data scientist must conduct organisational diagnostics to identify the key domains they need to tap into for relevant research questions. Unlime data analysts who are majorly concerned with analysing and processing available data to draw insights about predetermined goals, a data scientist's role entails identifying the appropriate research questions followed by the datasets that can provide potential insights into the research questions.
- Collecting Data from Diverse Sources: In certain cases, data scientists are also required to collect the data needed for their analytical purposes, i.e. they need to collect either primary or secondary data from various sources to obtain a dataset and further perform the analysis upon it. While data collection in most cases may not be a mandatory job responsibility of a data scientist (as organisations often have large secondary datasets available for analysis), certain unique goals or research questions may require collection of data to draw insights from.
- Systematic Data Processing: This is one of the central aspects of the role of a data scientist. Data scientists regularly indulge in cleansing the data, preprocessing the unstructured data, validating it before analysis, processing it and mining it further for finding business-oriented solutions from existing datasets.
- Data Mining: The major processing and analysis of data results from the process of data mining, wherein the data scientist uses a number of softwares and data mining algorithms to process the available dataset and understand its patterns, idiosyncrasies, discrepancies and more to develop meaningful insights. Further, they also indulge in developing algorithms for machine learning as well as predictive models for training AI models and softwares for future data analysis.
- Drawing Data-Based Conclusions and Insights: Based upon data analysis and processing, the results obtained are further subjected to analysis and interpretation to draw meaningful conclusions which can be used for business development and growth.
- Communicating Data Insights to Key Stakeholders: A very important job responsibility of a data scientist is to analyse data and further present the findings to key stakeholders in the organisation, such as the top management, the investors, the shareholders, the employees in certain cases as well as the customers (if the need arises). For this, the data scientist must possess significant skills in data visualisation (making the data understandable by stakeholders who may not necessarily be adept at statistics or analysing statistical findings) as well as communication.
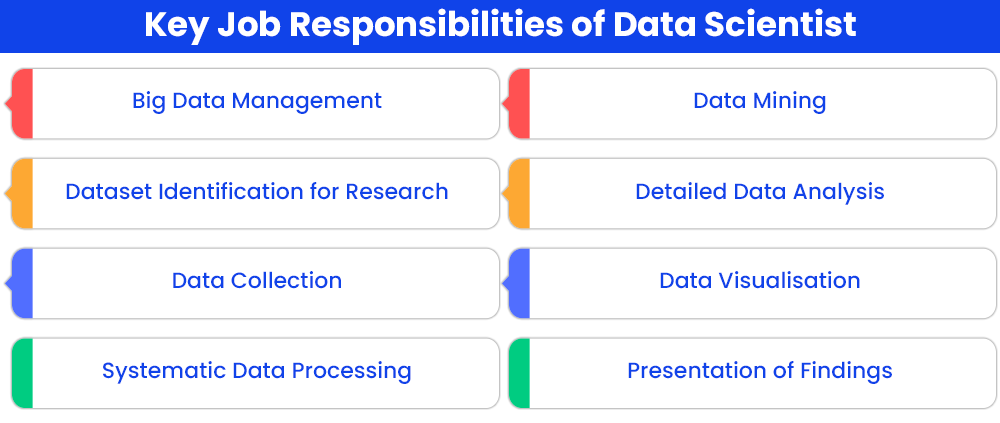
As is suggestive from the very job title, the job responsibilities of a data scientist are quite vast and dynamic, ranging from creating pertinent research questions for business cases and growth to processing of data and from data analysis to data visualisation and presentation to stakeholders. Data science is a diverse and dynamic job field, however at the heart of it lies significant data handling, an arena which you need to be proficient in for pursuing this career field.
Key Skills Needed to Become a Data Scientist
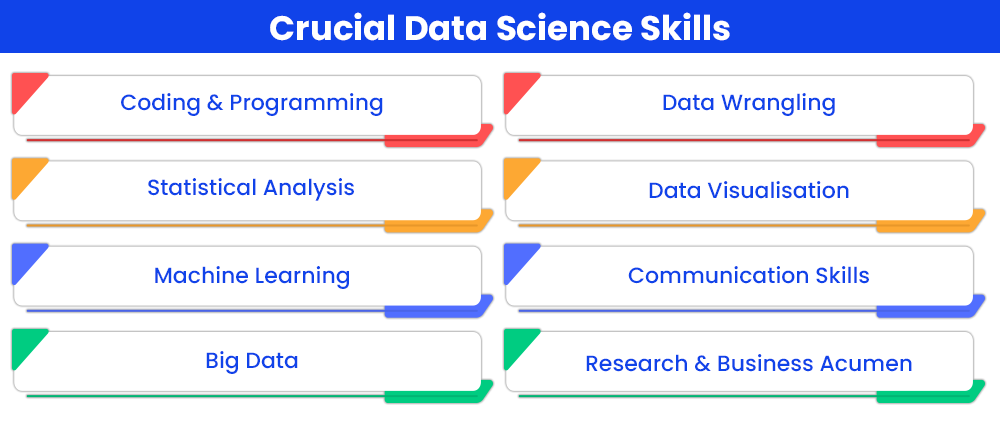
Data science being a highly technical field mandates the aspiring candidate to possess certain key technical skills in domains like coding, predictive analysis, big data analysis, ML and deep learning etc. However, the notion that data scientists do not require soft skills for their job role is a myth. There are certain key soft skills that are important for stakeholder management (an important aspect of data science job roles).
Certain key skills needed to excel in the domain of data science have been elaborated upon below.
Technical Skills
In addition to having requisite qualifications needed to practise professionally as a data scientist, one must also possess a host of robust technical skills related to the following areas to perform the work responsibilities efficiently:
- Coding and Programming: Coding and programming knowledge is highly crucial to developing requisite skills of data science. Knowing programming languages like Python, C++, R etc. can prove to be highly crucial to success as a data scientist.
- Statistical Analysis & Probability Analysis: In the case of a field highly driven by data, possessing strong skills of statistical analysis, distributions, statistical tests and their uses, regression and so on is central to being able to make meaningful interpretations from data. Related mathematical skills important for data science include principles of multivariable calculus and linear algebra.
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning: Machine learning and deep learning (a subdomain of machine learning) skills are critical to creating effective models that can statistically test and serve data insights. Relevant skills include k-Nearest Neighbors, Naive Bayes, SVM, Decision Forests etc.
- Big Data: Handling big data and meaningfully engaging with such data through data analysis, mining, data processes, data engineering, data algorithms etc. are key competencies required for data scientists to possess.
- Data Wrangling & Database Management: Data scientists need to regularly engage with vast datasets and hence handling databases effectively, processing data and wrangling data (identifying discrepancies and imperfections in existing datasets) are important skills for them to possess.
- Data Visualisation: Once key statistical insights have been prepared by running thorough data analysis, the data scientist must present the results in a manner that is easily discernible by stakeholders not necessarily proficient in statistics. For this, a data scientist must possess data visualisation skills in realms like ggplot, d3.js., Tableau, matplotlib etc. which can help them professionally prepare data visualisations to display their findings.
Non-Technical Skills
In addition to the conventionally valued technical skills needed to thrive as a data scientist, certain non-technical and soft skills form an important section of the needed job competencies. Mentioned below are a few of the soft skills and non-technical abilties important for data scientists to possess.
- Analytical Aptitude: Analytical aptitude is a non-technical skill which is required for the profession of data science. Analytical aptitude across a number of domains are important for a data scientist to be able to identify lacunae in organisational functioning and business as well as analyse data effectively to draw relevant insights and develop solutions.
- Critical Aptitude: Similar to analytical aptitude, a critical aptitude is helpful in understanding datasets, identifying imperfections and discrepancies in data, drawing critical insights from results of analysis as well as identifying potentially useful business-oriented solutions based on obtained results.
- Communication Skills: The communication skills of a data scientist are highly instrumental in the communication of findings based upon data analysis. After extracting relevant data insights from datasets, the results found must be communicated to the stakeholders of an organisation or a client. For effectively articulating the data results, the data scientist needs to be both well-articulated as well as proficient in convincing, explaining and negotiating in certain cases. Thus, communication abilities and people skills become central to the job role of a data scientist.
- Research Skills: Research acumen as well as an interest in developing research studies, identifying potentially useful research arenas for an organisation’s business growth and delineating the required steps for conducting the data analysis are crucial for a data scientist to sustain in their job role for a prolonged basis.
- Business Acumen: In addition to a prowess in research and data analysis, data science, from a business development perspective, the acumen for identifying potential channels for business growth is important. Thus, having a business and growth-oriented perspective while researching is essential for a data scientist to possess.
- Problem-Solving Skills: After identification of problem areas and insights based on data analysis, devising further business data-based solutions to guide business growth are also a part of the profession of data scientist. Thus, having robust, creative and innovative problem-solving skills are beneficial to further one’s success as a data scientist.
While a host of skills are needed to sustain and thrive in the career of a data scientist, there are a number of ways in which you can hone these skills. Technical skills can be developed right from when you are a student in school, which can provide you with a strong basis for future professional endeavours.
What is the Minimum Eligibility to Become a Data Scientist?
If you are a student enthusiastic about data science or a professional wishing to switch your career to the field of data science, then there are certain minimum qualifications you must possess to practise professionally in the field. These qualifications have been mentioned herein:
- To become a data scientist, a candidate must have a valid, completed Bachelor’s degree from a recognised higher educational institution, in either Mathematics, Computer Science, Statistics or Engineering.
- Further, the candidate must possess the requisite skills for data science such as strong programming, data mining, data wrangling, analysis skills.
- Organisations often prefer candidates having postgraduate education in training in data science, either in the form of a degree or an upskilling course in the specialisation of data science.
Additionally, candidates with experience in the data science industry are valued over candidates who lack working experience in the field. Additionally, it must be noted that the profession of data science usually includes highly-educated individuals, usually having at least a PG degree in data science or a PHD in many cases. Thus, while a Bachelor’s qualification may provide you with entry level job opportunities in data science, you must upskill yourself with relevant qualifications over time to climb the career ladder.
How to Become a Data Scientist: Step-by-Step Career Trajectory
In your career or academic journey, you may recognise your enthusiasm to become a data scientist at different points of time, for instance, while you are a school or college student, when you are pursuing postgraduate education or even when you have already ventured into the professional domain in a technology or ITES organisation.
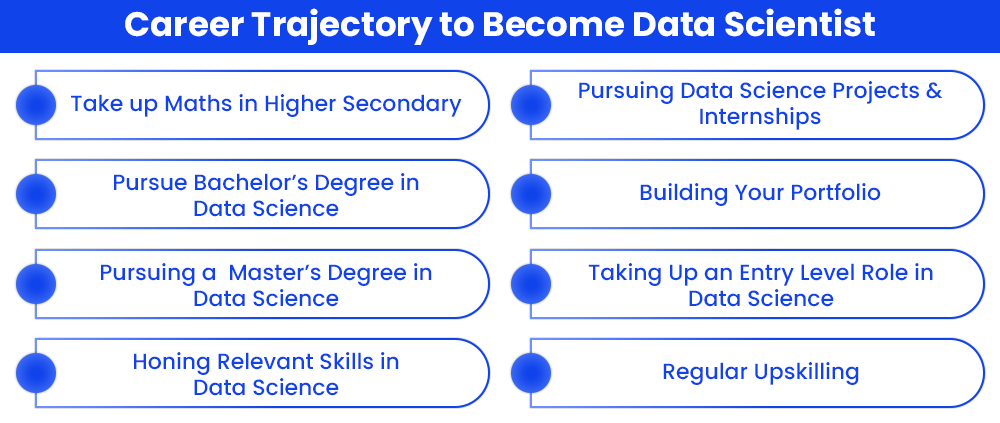 However, it must be reiterated that it is never too late to start a career in data science, as with the requisite skills set and qualifications, you can explore lucrative job opportunities in this industry. Provided below is a detailed step-by-step guide for you to consider if you are a data science aspirant and wish to kickstart your journey in this field at any stage of your education/career.
However, it must be reiterated that it is never too late to start a career in data science, as with the requisite skills set and qualifications, you can explore lucrative job opportunities in this industry. Provided below is a detailed step-by-step guide for you to consider if you are a data science aspirant and wish to kickstart your journey in this field at any stage of your education/career.
Step 1: Mathematical Focus in Higher Secondary Education
Data science as a field of study requires the extensive knowledge of domains such as calculus, algebra, statistical principles, regression, probability etc. which are advanced concepts in mathematics.
Hence, if you are currently a school student or a professional wishing to venture into the profession of data science, you should ensure that you have studied subjects such as Mathematics and Computer Science (or Informatics Practices) at the higher secondary level, i.e. class 11th and 12th. Candidates venturing into the field must have a stream background of mathematics, and preferably Physics, Chemistry along with Computer Science. Although in certain cases, students from other streams of education are eligible to pursue data science, mathematics is usually demanded as a compulsory subject in all cases.
Step 2: Earning a Bachelor’s Degree in Data Science
If you are a student who has already completed their school education and are now researching educational options for UG education in data science, then the most preferred career trajectory is to take up a Bachelor’s degree course in the relevant discipline (science, mathematics, engineering or statistics) with possibly a specialisation in data science or a related domain.
There are a number of degree courses considered valid to pursue data science as a career. While some of them are purely technical degrees that allow advanced education in data science, such as a B.Sc, a BCA or a B.Tech, there are non-STEM degree courses that allow one to develop data science skills and knowledge but from a business-oriented perspective–such as a BBA or a B.Com in data science.
Enlisted below are a few of the relevant Bachelor’s degrees along with their specialisations that you can consider pursuing for a career in data science.
|
Undergraduate Degree Course |
Available Specialisations |
|
Bachelor of Science (B.Sc) |
|
|
Bachelor of Computer Application (BCA) |
|
|
Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech) |
|
|
Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) |
|
|
Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com) |
Step 3: Earning a Master’s Degree in Data Science
If you are a candidate who has already completed their graduation and are now exploring opportunities for growing your career in data science, then pursuing postgraduate education is the next step in your career journey to consider. For instance, after having garnered a foundation in data science in graduation, you can enhance your knowledge of the field at an advanced level by taking up a Master’s degree course in a relevant specialisation.
Conversely, if you have a Bachelor’s degree in a technological or STEM discipline but lack expertise in data science, then taking up a Master’s degree course can allow you to develop and hone your data science competencies further.
Enlisted below are a few of the technical (MS, MCA, M.Tech) courses and non-technical professional courses (PGD, MBA, EMBA) that one can consider to kickstart their formal education in data science.
|
Postgraduate Degree Course |
Available Specialisations |
|
Master of Science (M.S) |
|
|
Master of Computer Applications (MCA) |
|
|
Master of Business Administration (MBA) |
|
|
Executive MBA |
|
|
Postgraduate Diploma (PGD) |
Step 4: Honing Relevant Skills in Data Science
In addition to pursuing a formal qualification course in data science, possessing proficiency in the working skills and domains of the field are highly crucial. Data scientists need to possess a host of skills related to program development, machine learning, data visualisation etc. to be able to perform the operations of data analysis efficiently.
Thus, it is important to start practising the key skills of data science including working regularly with data mining, programming and data visualisation tools to gain familiarity with such softwares and increase one’s knowledge and hands-on skills in the same.
Step 5: Complete Data Science Projects & Internships
Alongside formal education, an effective way of growing one’s skills and prowess in data science is to regularly take up relevant projects in the field. In certain UG and PG degrees, projects and research in data science is mandated by the curricular requirement. They can provide an excellent avenue to put your theoretical knowledge to practice and apply concepts of the subject to actual scenarios. In addition to pursuing course-mandated projects, one can take up additional projects depending upon their interest and proficiency in data science, which is beneficial for both skill development and portfolio building.
Similarly, while you are completing an educational course in data science, exploring internship opportunities is an excellent strategy to upskill yourself and gain professional exposure. There are a large number of paid as well as unpaid internships which can provide you an excellent outlet for hands-on experience and professional exposure.
Step 6: Building Your Portfolio
In a fast-paced professional world where competition is soaring by the hour, it is important to strategically showcase your skills and expertise and develop a profile that outlines your accomplishments in the field effectively. Portfolios are an excellent tool to start preparing right from college to highlight your proficiency and excellence in data science.
Pursuing formal education in data science, highlighting major academic accomplishments, highlighting extracurricular achievements related to data science, regularly pursuing projects and internships in data science, researching in the field etc. all contribute significantly to the process of building an appealing and strong profile that can enhance your future professional opportunities.
Step 7: Get an Entry Level Job Role in Data Science
Like any other professional domain, the field of data science also comprises a variety of job opportunities starting at entry levels and escalating to executive levels. Securing a job role in data science can be a challenging and stimulating process, for which you must maintain a persevering and resilient attitude.
You can start exploring career opportunities at various levels as a data scientist. While it is most likely that as a fresher you would secure an entry-level position in a tech firm, you should still apply to data science jobs at various levels to gain exposure to the selection procedures for various data science opportunities. Furthermore, considering the growing competitive levels for a lucrative field like data science, it is very likely that a candidate might have to apply to a number of opportunities before bagging an opportunity. Thus, it is important to continue exploration of job opportunities without losing hope.
Step 8: Gain Experience and Upskill for Career Escalation
If you are a professional already practising as a data scientist or looking to switch to this career domain, then upskilling yourself is necessary for both securing the right job options and escalating in one’s career. There are a number of available options for professionals to consider if they want to hone their data science skills further. There are courses available in the online as well as offline, face-to-face mode to consider. The durations, flexibility of learning and level of courses available make executive education in data science highly appealing to take up.
Enlisted herein are a few of the certification and upskilling courses such a diploma and bootcamp courses that you can consider as a working professional in the field for upskilling.
|
Certification and Upskilling Course |
Available Specialisations |
|
Job-Guaranteed Certification Courses |
|
|
Pay-After Placements Certification Program |
|
|
Bootcamp Program |
|
|
Professional Certificate Course |
|
|
Professional Certificate in Data Visualisation |
|
|
Professional Certificate in Big Data |
Careers in Data Science and Its Scope in the Future
In addition to pursuing a career in this profession as a data scientist, there are a number of related roles as enlisted below that you can explore after pursuing formal education in data science. Data science focuses its emphasis on the holistic processing and analysis of big data to draw insights relevant to business growth and development. There are a number of related fields like data analytics and business analytics, artificial intelligence, data engineering etc that incorporate insights and knowledge of data science. A few of the prospective career domains in and related to data science that you can consider pursuing have been enlisted herein.
- Data Scientist: The role of a data scientist in an organisation is related to utilising vast datasets to arrive at meaningful insights which can be further utilised to drive business growth endeavours. As professionals, they are concerned with the all-round development of data-driven solutions starting from identification of datasets to providing visualised data insights and further suggesting solutions to drive growth and development.
- Data Architect: Data architects are involved in aspects of creating softwares and database systems. They are involved in a number of tasks including the development of new software and applications, information systems, data migration and so on.
- Data Analyst: A field commonly confused with data science, the role of a data analyst is centred on aspects related to the analysis of already collected primary or secondary data, effective storage of the data and insights on a database management system for future reference and developing data collection systems.
- Business Analyst: Business analysts are mainly focused on the analysis and interpretation of past business data of an organisation to derive solutions for current business growth. They are also commonly involved with aspects like overall planning, monitoring and regular data inspection to identify and amend existing business plans.
- Data Engineer: This job role is concerned with the management of complex big data with respect to building analytical tools, engaging in data assembly, data processing, data extraction, data cleansing and transformation.
- Data Administrator: The job domain of data administration includes aspects such as database designing, database updation, development of new database systems and data handling systems, securing databases and so on.
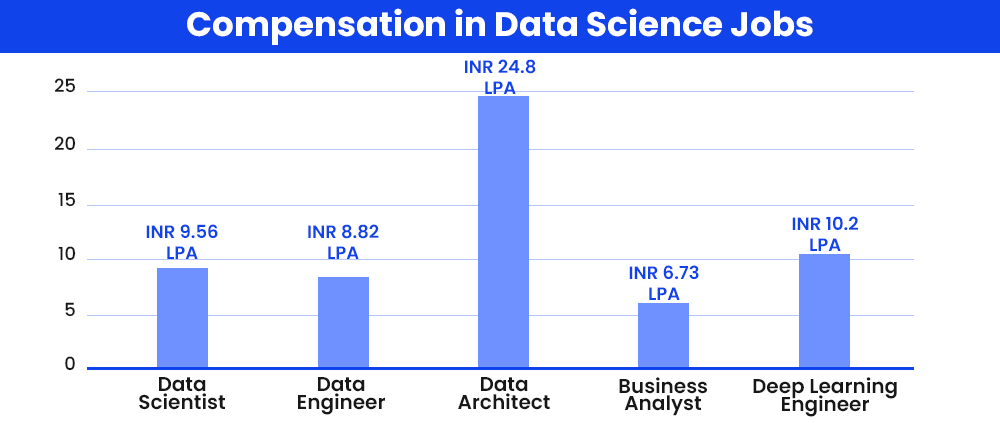
Provided here is a summarisation of the current compensation trends in the field of data science and related job domains. The enlisted figures reflect compensation in the field as provided in India to a professional with nearly 2 to 3 years of relevant job experience.
|
Job Role |
Average Salary in India (per annum) |
|
INR 9.56 LPA |
|
|
INR 8.82 LPA |
|
|
INR 5.03 LPA |
|
|
INR 24.8 LPA |
|
|
INR 6.73 LPA |
|
|
INR 5.61 LPA |
|
|
INR 8.24 LPA |
|
|
INR 10.2 LPA |
Conclusion
As can be seen, the job domain of data science is a lucrative and appealing field where one can expect to build a prosperous career especially in the future considering data science is gaining traction in organisations and professional domains. There are a diverse number of jobs one can explore as a data scientist and develop a successful career in the domain through gaining relevant qualifications and upskilling oneself to stay updated in the field.







![What Is the Scope of Data Science In India? [Latest 2026]](https://d1aeya7jd2fyco.cloudfront.net/blog/what-is-the-scope-of-data-science-in-india.webp)









