Expert Interviews
- University Reviews
- Career Guide
 Video Counseling
Video CounselingImportant Facts
- Ask any Question - CV Forum

Management Process: Definition, Steps & Functions [2026]
College Vidya Team Jan 4, 2026 7.5K Reads

A raging word in the mouths of students, corporations, and working professionals today is Management. Whether it be choosing a career domain or escalating up your career ladder, management is a word that comes to mind. But before it became a popular choice for higher education, it was a process involved in virtually all aspects of working in a group.
Did you know that the history of management dates back to before the birth of Christ? Or that management is not just a raging career option today but was an ancient practice for organized work? If you are interested in knowing more about the process of management, definition of management, functions of management, and its importance, then you are at the right place.
In this blog, we have broken down the entire process of management and various aspects related to it for you, in full detail. Continue reading till the end to find curated experts’ opinions from our College Vidya experts about the process of management.
What is Management? Definition, Examples, and Meaning of Management
Management as a process and practice has been defined by different theorists in various ways.
Management has been defined as the “process of designing, and maintaining an environment in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims” by Harold Koontz and Heinz Weihrich.
From this definition, one can understand that in the simplest terms, management refers to the process in which a group works, under systematic direction, towards efficiently achieving shared goals. The entire management process revolves around the central aspect of working and utilizing resources efficiently with the ultimate aim of goal completion.
A simple example of management will be a teacher managing and arranging a committee of students to conduct an annual day. This would include
- A Group: in this case includes the group of students who will be involved in the performances and arrangements of the annual day.
- A Shared Goal: in this case is the smooth conduction of the school's annual day.
- Resources: in this case involves the various monetary resources, human resources (students and teachers who will perform and organize the function), and the various costumes and props involved in the annual day.
This is a simplistic example of how management as a process works, more nuanced examples of management include corporate management, financial management for a company, management of a team in a firm, etc. From hereon, we will discuss management as a process in the context of professional environments and companies.
Explorer Our Popular Diploma Management Course
Concept of Management
To understand the concept of management, a Threefold Model of Management has been developed by Harbison and Myers, which has been explained in simple terms for you here:
- Management as an Economic Factor: As per this approach, management is an essential factor that is involved in the economic aspects of the development of any organization, region, or country. So, management and economic development go hand in hand- if the economic improvement of a company/nation is to be improved, then the need for management will also grow. For example, management is important to ensure efficient functioning and goal completion, if a company wishes to grow itself and maximize profits, then it must also focus on management.
- Management as an Authority: From a historical perspective, the domain of management developed as a form of authority in an organization. With numerous developments and evolutions in management, the approach has been refined a lot today and the approach has changed from purely an authoritative one to a mix of democratic, participatory, and constitutional approaches to management.
- Management as a Part of Class and Status System: From a larger social perspective, management as a process represents a class and status system. Being aimed at increasing the efficiency of work to ultimately achieve goals, management needs to be a procedure of much strategy and planning, all of which require a greater intellectual involvement. Thus, as a result, management is viewed as constituting a system of class and status due to the supervisory role it plays in organizational functioning. The modern corporate viewpoint wherein career escalation is often viewed as climbing up from entry-level or middle positions to higher and top-level managerial positions is rooted in this approach of management.
Objectives of Management- What Does Management Seek?
When talking about management, the understandable question that arises is- why need management at all? What is the objective of management as a process and what does it seek as the ultimate goal? As you might have already guessed, management ultimately revolves around the fulfillment of a shared goal. But management is much more than just goal completion, it is the efficient and cheapest way of goal completion (Henry Fayol).
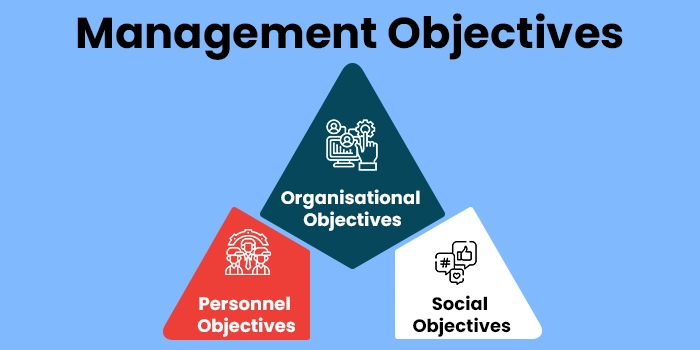
The basic objectives of the management process are listed here.
- Organizational Objectives of Management: This includes the various objectives and goals that management seeks to achieve from the company perspective, i.e. at the organizational level. These include the utilization of minimum resources to produce the maximum outputs and production, increase the productivity of an organization, increase the efficiency of work, maintain quality, and maximize profits.
- Personnel Objectives of Management: Undoubtedly, the personnel, or the members involved in the process of management are one of the crucial aspects of management. So, an important objective of management is to also effectively meet the goals of the members of an organization, promote their personal development, increase their motivation levels, their productivity, boost their morale, maximize their potential, and so on.
- Social Objectives of Management: As already stated, the objective of management is not only to meet the goals of an organization but to do so in a way that ensures the larger welfare of society. For instance, at the social level, the objectives of management include improving the quality of life of people through efficient functioning, upliftment and betterment of the society through shared goal achievement, social justice by improving the quality of life of members of the society at large, and so on.
So, it can be said that the management of any work or organization works at serving the personnel objectives at the grassroots level, the organizational objective at the intermediate level, and the social objectives at a broader level.
Explorer Our Popular Certificate Management Course
| Advanced Certificate Management Course | ||
| Advanced Certificate In Digital Marketing | Advanced Certificate In Business Management | Advanced Certificate In Project Management |
| Advanced Certificate In Operation Management | Advanced Certificate In Corporate Communication | Advanced certification In Hospital and Healthcare Management |
| Advanced Certificate In International Business Management | Advanced Certificate In Power Management | Advanced Certificate In Oil & Gas Management |
| Advanced Certificate In Renewable Energy | Advanced Certificate In Industrial Saftey | Online Certificate Programs |
Features and Characteristics of Management- What is the Nature of Management?
Management as a process has certain unique characteristics and features of itself, which constitute the nature of management. Here we have enumerated the various key characteristics of the management procedure:
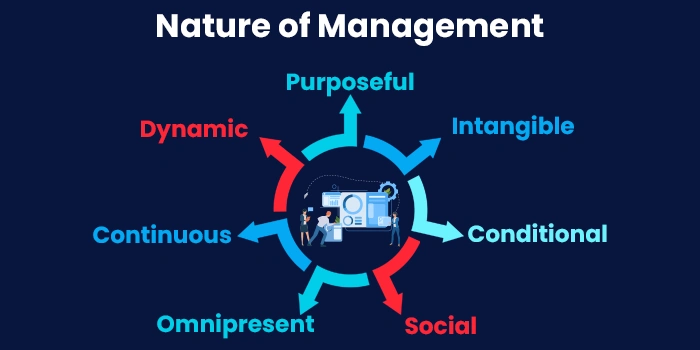
- Management is Multidimensional: Management as a process is involved not one but many dimensions of an organization. In this respect, it is a multidimensional discipline. It is involved with
- Management of Goals
- Management of Human Resources
- Management of Operations Involved in Goal Fulfilment
- Management is Goal-Oriented and Purposeful: Management as a process is goal-oriented. The entire idea of the managerial process is centered around successfully and efficiently achieving the goals of the company. All the operations and processes involved in management are directed toward meeting the goals of the organization, the personnel, and the society at large. So, management is purposeful and all its functioning is ultimately aimed at goal fulfillment.
- Management is a Dynamic Process: Management as a process, is dynamic. It is flexible, fluid, and situational, taking into consideration the unique context in which it must be efficiently used to meet organizational goals. So, it is not a static set of rules and approaches to handling operations and is constantly changing and evolving as per the needs and context of the environment in which it is functioning.
- Management is Intangible and Abstract: Management is a process and hence, it is not tangible in terms of a product. It is not a concrete tangible product but rather an abstract process that consists of numerous constitutional processes and operations, policies, goal-oriented activities, and so on. So, management is an abstract part of efficient functioning in a company and compliments the overall production and productivity of the organization but cannot itself be concretely seen or felt tangibly.
- Management is A Continuous Process: Management is an omnipresent and continuous process. It starts right from the strategizing of functions, job roles, and so on, to the effective implementation of the strategies, allocation of responsibilities to various individuals, effective utilization of resources, final production/service, evaluation of feedback and accordingly planning future endeavors. Management is a holistic process that is involved in every part of the efficient functioning of a company. So management can be considered as a continuous rather than discontinuous process, which plays an active although intangible role throughout all functions of an organization/company.
- Management is Conditional: This means that management is responsive to the specific conditions in which it must function. The situational aspects are taken carefully into account in a management process and it is accordingly tailored to meet the current needs and goals as efficiently as possible. So, management is not only dynamic, it is conditional and situational as well and it must meet situational needs and avoid constraints.
- Management is a Group Activity: Management is an all-encompassing process and hence it cannot be effectively conducted by a single person or authority. It is a group activity and a collective effort. It is needless to mention the active participation of each stakeholder and member of a company/organization is essential to make management successful and achieve the desired goals. So, it is a group activity in which individuals from various dimensions of company functioning come together to collaborate to ultimately increase productivity and bring together the required goals.
- Management is Omnipresent: Management is an omnipresent factor in any organized activity as we have already discussed. Management being a process that starts from the grassroots level and expands up to the overall supervision and conduction of projects, is involved in any basic group activity, be it a school, classroom, a company project, or a basic function arrangement and conduction. Management is omnipresent and ever involved with all parts of an organized group activity. So, management as a process has certain basic features that characterize it and explain its nature. It is important to keep these features in mind and effectively implement them in the effective functioning of a company or organization.
Levels of Management
As already discussed, management as a process is multidimensional and functions at multiple levels and domains. Moreover, it is a process that starts at the micro level or organized functioning and develops up to the broad functioning at a social and organizational level. So, it functions at several levels or functions. The functioning of management can be best described as functioning at 3 main levels:
- Operational Management: Operational management is typically the management of employees and operations at the grassroots level of a company’s functioning. This involves direct involvement with the human resources and assets of the company at a functional level to reach the company's goals. This level of management typically involves team heads and strategists who delegate individual goals to employees. Executives involved with the efficient goal achievement of a particular unit are included in this level of management. Operational managers are responsible for ensuring that the employees meet their targets and goals and that organizational decorum and rules are maintained at the team level.
- Middle Management: The intermediate level of management, middle management includes heads and leaders who are usually responsible for the efficient functioning of particular departments and divisions. They form a bridge between the top executives and the operational heads of various teams in the company. Their responsibilities include conveying the top-level goals and policies to the operational management, ensuring that teams and departments are working in sync, and by these goals, company policies are followed and upheld in the company, and that the departments are collaborating to maximize productivity and profits.
- Top Management: The top management of any company constitutes the top-most rung of the company’s authority, which usually includes members such as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Operating Officer, Chief Financial Officer (CFO), Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), etc. Such posts represent the top management level in a company and hence are involved in the overall company structuring, goal strategization, integration of employee goals with overall company goals, policy formulation and approval, etc.
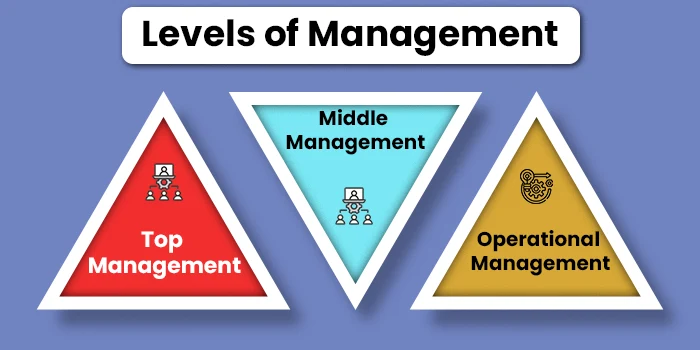
Effective management results from the integrated and in-sync functioning of these levels of managers in addition to the integration of various company, personnel, and social objectives.
Principles of Management
The French industrialist Henry Fayol proposed 14 principles of management which are rooted in the idea of organising work in a company to maximise efficiency. These 14 principles are:
-
- Division of Work: Efficiency and productivity of employees increases when the work is divided among the workers
- Authority and Responsibility: Managers should have authority over their subordinate members as it increases productivity. This is so because they have the authority over their team but also accountability and responsibility for the work performed under their supervision and authority.
- Discipline: Discipline is the cornerstone of efficient and organized company functioning and should be the core guiding value in any undertaken project or goal.
- Unity of Command: Every employee should have only one reporting boss to ensure organized work.
- Unity of Direction: Unity of direction means that the employees who are involved in the same project or who work together have one shared goal so that all the efforts and work of that unit are directed towards the same goal.
- Subordination of Personal Goals: Fayol proposed that for the maximization of the company’s profits and productivity, employees and members of the organization should give the utmost priority to the company’s goals and values and hold their personal goals secondary to the organizational goals.
- Remuneration: The monetary and non-monetary remunerations of the employees and members involved in the organization should be proportionate to their contributions and efforts to ensure social justice and equity in the organization.
- Centralization: This refers to the practice of the top management of any company as being unbiased and neutral.
- Scalar Chain: An organization should have a top-to-bottom line of hierarchy.
- Order: To maintain a decorous and efficient work culture, a company should have a well-defined and organized work order that is followed and maintained by the employees.
- Equity: The principle of equity in management is rooted in the idea of social justice. To improve the efficiency and productivity of a company, all its employees should be treated justly and with respect.
- Stability: The stability of an organization and consequently its production and efficiency grows when all the employees feel secure about their job. This enhances the trust placed by the members in the organization and increases their commitment towards it.
- Initiative: This principle is centered around the value of taking initiative and initiating change and innovation in a company. This is not only the responsibility of the leaders or managers of the company but also all the employees who are a part of it.
- Esprit de Corps: According to this principle, the management has the responsibility to boost their employees’ morale and motivation as well as support them regularly.
So, by running a management based on these principles, companies, and organizations can flourish and increase the productivity of the employees.
The Managerial Process- What are the Steps and Aspects of Management?
As a process, management can be thought of as consisting of 3 main aspects:
- The Social Aspect of Management: Being deeply involved with the human resources of any organization, management is concerned with the development and maintenance of various human relations. However, unlike random interactions between people, management must ensure that such interactions and human relations in an organization are relevant, professional, and productive from the perspective of the company.
- The Integrating Aspect of Management: Management plays the role of integrating the functions of various domains in a company. Management helps to integrate the human resources and assets, the monetary resources, and the operational aspects of an organization to produce the most efficient outcome.
- The Continuous Aspect of Management: Management is an ongoing process and is involved at every step of running an organized activity and group. Hence the management process plays a continuous role in a company as it keeps on assessing the situational constraints and adapting the company operations accordingly.
The management or managerial process consists of the following steps/ aspects:
- Planning: The first and foremost step of management is to plan and strategize the goals the organization must achieve, how to run operations to achieve them, optimize the use of various resources accordingly, and integrate the functioning of various employees and units accordingly.
- Organizing: After effectively planning the various aspects that will be involved in the management process, the next step is to organize the functioning of the various units involved in it. This involves the creation of a productive relationship between the various units involved in goal fulfillment, effective integration of these units, delegation of responsibilities to these units, and so on.
- Coordination: To maintain the organization's functioning, effective coordination between the various units, resources, and operations is needed. One of the prime aspects of the management process is that the functioning of various teams, and departments and the utilization of resources in the company should be well-coordinated and directed towards the same goal- fulfillment of the company’s objectives.
- Motivation: Just as the principle of management as being “esprit de corps” suggests, the role of management is not only to increase the production and profits of the company, it is also to motivate the employees and boost their morale. Good management is not only involved with goal fulfillment but also works towards the overall growth and welfare of its employees.
- Control: The managerial process in itself is involved with controlling the various aspects of functioning in an organization, although controlling is not the sole idea around which management is centered. But since management has a supervisory role to play, it indeed involves practicing a certain degree of control-whether it is in terms of control of operations involved in company functioning, control of the relation and authority functions between various departments of the company, or control of the use of various resources.
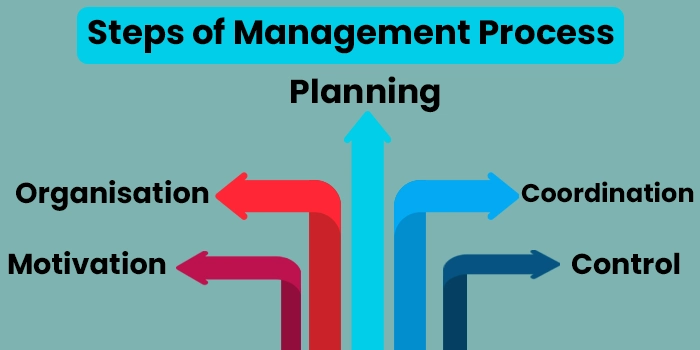
Hence, the managerial process has a holistic approach and covers several important steps and functions.
Management Process in a Business: The Business Process Management (BPM)
When talking in the context of a business, it can be said that management is aimed at fulfilling the business goals, which mostly include the maximization of business profits and bringing about business growth. The management process in a business is often called “Business Process Management”, abbreviated as BPM. This process is directed at 3 main aspects of business development, namely.
- Monitoring the various business procedures
- Analysing the business procedures carefully to find problems as well as areas of improvement
- Optimizing the business processes accordingly to bring about innovations and changes
All the above aspects of BPM start from the planning process until the end of the implemented plans to achieve the needed business goals. The process is continuous and fluid, developing and evolving regularly as per the situational and contextual demands of the business environment. As a process of management specifically aimed at businesses, the steps involved in BPM vary slightly from the general management process. Here we have enlisted the various steps of BPM with examples for you:
- Design: The very foundational step of an effective BPM is a well-designed plan about how you wish your company/business to be managed. For this, collect data about the existing business flow systems and work divisions in your firm. This data can be further used to accordingly design and implement strategies.
- Model: To integrate your existing business design with your business goals and plans, prepare a layout of business processes and evaluate how you can amalgamate and accordingly adjust changes that can blend your existing business flow with your desired business flow. A well-structured BPM model helps managers to effectively redesign and adjust changes for business growth.
- Implement: After a business design and usable business model have been developed, the next step is to implement the changes accordingly and evaluate their effect and efficiency. It is preferable to start your business change implementation in a small group first (much like a pilot study) following which you can expand it to other teams and units involved in your firm.
- Monitor: A BPM is a continuous process and hence it involves continuous evaluation and monitoring to ensure that the processes are being managed effectively as well as whether they are useful in the context of business growth and goals to be achieved. A nuanced analytical approach is needed in this regard.
- Optimise: Like any other managerial process, BPM is also a dynamic and fluid process. Hence, it involves continuous optimization and tweaking to achieve the desired effect. Hence, as per the results of the evaluation and monitoring of the various business processes, managers must accordingly optimize functioning and operations to meet demands.
Hence, BPM is an up-and-coming domain of management that is gaining rising importance among business and professional circles for growing the business and maximizing profits.
Functions of Management- What are the Roles Performed by Management?
Management as a process is indispensable to the efficient functioning and running of a company or any organized work. But you may wonder why so. This is so because despite being an abstract and intangible process, it performs several central functions that make it one of the most crucial aspects of the success of a company.
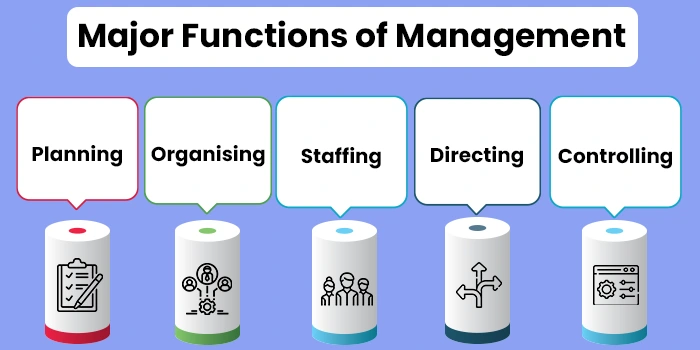
According to Koontz and O'Donnell, management as a process has 5 main functions:
- Planning: As already discussed above, the very process of management starts with a plan. Management is a very purposeful and goal-oriented process and hence managers perform the important task of planning at several levels- planning and deciding upon the goals of the company, formulating company policies, planning the division of responsibilities between units and teams, planning an overall strategy for effective implementation and planning for effective utilization of resources.
- Organizing: Management as a process also includes the organizational function. For example, since it is a purposeful, continuous, and conditional process, it involves organizing work and operations such as delegation of responsibilities, upholding company policies, effective implementation of tasks, coordination of units, etc. All such functions can be broadly categorized as seeking to ultimately increase the organization in the company functioning.
- Staffing: Since management must ensure that some efficient human relations and relationships enable increased productivity and maximization of company profits, it also has the role of developing a team of employees that are dedicated and suitably meet the needs for achieving the company goals. For this, management must focus on staffing functions to recruit, hire, and develop the needed personnel of the company. Management is hence deeply involved with the team building and staffing function of a company.
- Directing: Management does not only involve the supervision and optimization of tasks and operations but also the human resources involved in the processes. Hence, good management also performs the key function of providing a sense of direction to the employees as well as motivating them toward personal and organizational growth. Effective management is closely related to inspirational leadership.
- Controlling: As already discussed, management as a supervisory process also involves some exertion of control. To seek effective goal achievement, all activities, interactions, and operations must be controlled effectively. Moreover, management also involves an authoritative role as it includes supervision of employees involved with a company as well as the various operations they perform.
So, management indeed has multiple crucial functions that it performs, be it from the very formulation of company goals and vision to effective implementation and smooth running of various operations.
Scope of Management- What Areas Can be Explored in this Field?
Management as a discipline has a vast scope. Be it from the vast number of domains in which management is actively involved to the various subdomains in which managerial functioning can be divided, the scope of management is vast and diversified. Moreover, with the increasing awareness about the role well-planned management plays in company growth and development, this scope is only expected to grow further.
Career domains within management are diverse and numerous. Not only are such fields handsomely paid and compensated, but the scope for career escalation in management is significantly high as well.
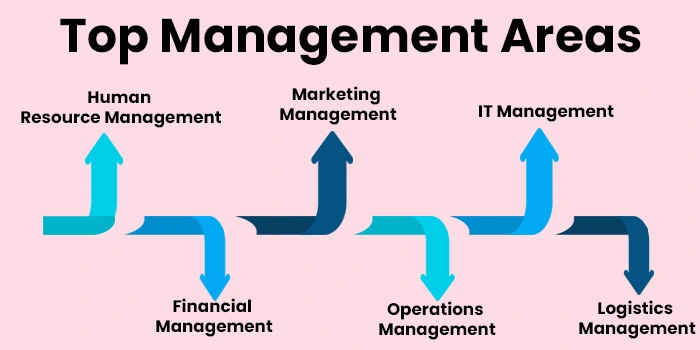
Hence, if you are desirous of exploring the domain of management further and developing a career in it, then there are a multitude of options available for exploration. Here we have highlighted some of the most prominent domains of management today.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): This is the domain of management that is involved with all the aspects of managing the human assets of a company. So, the functions that HRM is involved with include talent acquisition, recruitment and placement of employees, employee training, grievance handling, human resource development, managing organizational functioning, labor laws, managing human relations in the company, and so on. So if you are interested in interacting with employees and managing the human aspect of organisational management then HRM is the field for you.
- Financial Management: This domain of management is responsible for handling and managing all the financial aspects of a company or business. This includes various responsibilities such as financing, auditing company expenses, maintaining accounts, managing cash and credits, taxation, cost analysis, and much more. So if you are a financially oriented person who is fascinated by numbers and figures, then this might be a desirable career option for you.
- Marketing Management: Marketing management, as the name suggests, is involved with various aspects of marketing and advertising a company. This involves various aspects such as effective advertising of the company, sales hacking, brand management, brand presentation, strategic planning of marketing goals for the company, digital marketing, social media handling of company accounts, use of marketing to effectively grow the company, and so on. This field has a vast creative scope and is ripe with opportunities to adopt innovative ideas for marketing.
- Production and Operation Management: Production and Operation Management is concerned with handling the various processes and grassroots as well as broader operations functional for company growth. This includes handling aspects such as resource planning, quality management, procurement of goods and services, operations of various units of a company, and so on.
- Quality Management: Quality management as a domain of management is involved with ensuring that the various operations, human relations, and business functions of a company are being handled and optimized to maintain the company’s standards of quality. The main idea is to maintain and uphold a desired level of excellence and efficiency so that goals are effectively achieved.
- Strategic Management: Strategic management is an all-around aspect of management that involves the overall assessment of the company’s goals and resources to accordingly strategize the various aspects of management like plans of future action, delegation of responsibilities, implementation of those plans as well as optimum use of company resources. Strategic management as a subdomain of management covers a wide scope in itself since strategic management can be needed at virtually any step, department, and area of management.
- Logistics Management: Logistics management involves the supervision and regulation of the various operations involved in the implementation of a complex procedure. The main aim of it is to ensure the efficient flow of goods and services as well as storage and supply of them. Logistics and supply chain management are two closely related areas of management in which students can explore a variety of career opportunities.
- IT Management: As the name suggests, IT management is involved with the effective management of the various technological aspects involved in the smooth and efficient functioning of a company or organization. IT managers supervise a wide variety of tasks and aspects of company functioning such as database administration, technology management of a company, software engineering aspects, IT privacy and cybersecurity, and much more. This is a highly popular and in-demand area of management in contemporary times of a technology-driven industry. MBA In Information Technology.
Explorer Top Management Specialization In Demand 2026
What College Vidya Thinks?
Our career experts and experienced mentors reckon that management as a career can not only be highly successful owing to the plethora of career choices available but can also be highly useful and conducive to your personal development. Management as a career option gives you the chance to explore your future options in both the private and public sectors. Not only this, its high professional demand helps you choose the best job option in your area of interest.
Management careers can be explored in top global MNCs, business houses, corporate sector as well as reputed government sectors. These fields are all handsomely compensated and with the right guidance and ambition, can help you navigate smoothly towards career escalation.
But more than that, what a managerial career does is that it helps you to work towards your skills and abilities in several areas. Management puts you in situations where you learn to interact efficiently with people involved at various levels of an organization, you learn to make crucial decisions regarding company functioning and use of monetary and non-monetary resources, manage micro and macro-level operations, and much more. All such practices help you hone your skills such as decision-making and problem-solving ability, analytical and critical ability skills, communication and persuasion skills, and much more. This makes management a career worth pursuing.
We at College Vidya strive to provide you with the most unbiased and insightful guidance that can build a successful career. We understand your ambitions and needs and provide you with customized support in choosing the higher education course that is the best fit for you.
Importance of Management- Why Do We Need Management?
If you have read the piece up till here, you are probably already aware that management is a crucial aspect of any company, and is the cornerstone to achieving the company's goals and production needs. Here we have listed some of how management is a significant and important part of organizational functioning-
- Management is purposive and hence it helps in achieving the goals and objectives of the company, personnel, and society at large.
- Since management includes careful planning and strategizing, it ensures the optimum and just use of the company's resources, both monetary and nonmonetary.
- Management is an omnipresent and holistic procedure and hence it increases the efficient functioning of a company.
- Effective management is not only focused on the goals and needs of the company but it also integrates the personal and group goals of the employees involved.
- Since it is dynamic and evolving in nature, it increases the adaptability and dynamics of the group as a whole.
- One of the major principles of management is to increase the motivation of the employees. Good management seeks the growth of the company as well as the personal and professional growth of the employees in the company.
Our Top Management Article
Conclusion
So, understandably, management is one of the most crucial aspects of any organized activity, especially in the context of an organization or a company. In professional spheres, the role of management as a process is indispensable. Management functions at various levels, sometimes tangible and sometimes abstract.
Effective management is fundamental to successful goal achievement by any organization irrespective of its level of functioning. Management careers are highly demanded today and there are a vast number of domains within the discipline to explore and venture into.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Management refers to the process of designing, and maintaining an environment in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims, as defined by Koontz and Weihrich.
Management can be of 3 broad types, on the basis of the level at which it operates- executive management (top-level management), middle management, and operational management (microlevel management).
The 5 main processes involved in management include planning, organizing, coordination, motivation, and control.
The 3 levels of management are operational management (lowest grassroots level of management), middle management (bridge between top and lower management), and executive management (top level of management consisting of company heads and executive officers).
Management means a process in which a group works, under systematic direction, towards efficiently achieving shared goals. It includes a number of aspects such as planning, organizing, supervision, strategizing, regulation, analysis, and adaptation as per the needs of the hour.
As per the definition proposed by Koontz and Weihrich, management is the “process of designing, and maintaining an environment in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims”.
As proposed by Koontz and O’Donnell, management has 5 main functions- planning, organizing, staffing, directing (or leading) and controlling.
Management is needed because it is one of the most important aspects to ensure that the goals of a company are effectively achieved. It performs a number of important roles such as ensuring the optimum use of resources, ensuring fruitful and cordial interactions between the various individuals in the company, effective delegation of responsibilities in a company, strategic planning and implementation of operations, and much more. Management is needed to ensure that the company and its employees grow and develop efficiently.
Management has a vast scope and there are a large number of career options available in this field such as human resource management, financial management, marketing management, operations and supply chain management, logistics management, IT management, blockchain management, and much more. Interested students can explore their options and take up degrees or diplomas or even short-term certification courses in management to develop a successful managerial career.

Idea Alchemist / Concept Creator / Insight Generator
We are an online education platform where users can compare 100+ online universities on 30+ X-factors in just 2 minutes. With an active CV community, we have transformed online learning to quite an extent. With the CV Subsidy scheme, we contributing to GER in India while helping our learners with their finances in their “Chuno Apna Sahi” journey!
Every query is essential.
Our team of experts, or experienced individuals, will answer it within 24 hours.
Recommended for you
Tired of dealing with call centers!
Get a professional advisor for Career!
LIFETIME FREE
Rs.1499(Exclusive offer for today)

Pooja
MBA 7 yrs exp

Sarthak
M.Com 4 yrs exp

Kapil Gupta
MCA 5 yrs exp
or



Career Finder
(Career Suitability Test)
Explore and Find out your Most Suitable Career Path. Get Started with our Career Finder Tool Now!
ROI Calculator
Find out the expected salary, costs, and ROI of your chosen online university with our free calculator.

